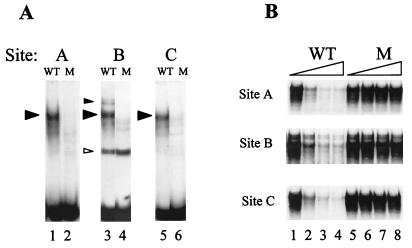
FIG. 2.
Mutations of the three rat OC Cbfa sites result in loss of Cbfa binding. (A) Formation of the osteoblast-specific complex from nuclear extracts of ROS 17/2.8 cells compared with oligonucleotides containing WT sequences representing Cbfa site A (lane 1), site B (lane 3), and site C (lane 5) and mutated (M) Cbfa sequences of sites A (lane 2), B (lane 4), and C (lane 6) in gel mobility shift assays. Cbfa complexes are indicated by solid arrowheads. A nonspecific complex (site B) is indicated by an open arrowhead. (B) Site A, site B, and site C show corresponding competition assays for each Cbfa site with the WT sequence as probe with increasing amounts (0, 20, 60, and 80×) of either WT oligonucleotide (lanes 1 to 4, respectively) or Cbfa site-mutated oligonucleotides (lanes 5 to 8, respectively) as the competitor.