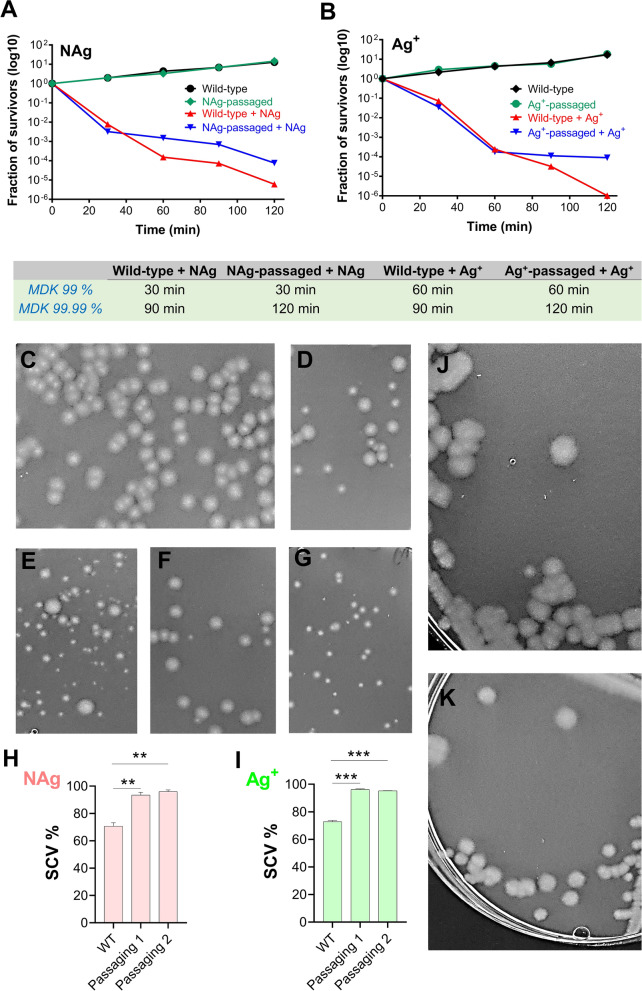
Fig. 4.
Persistence to silver and the formation of small colony variants (SCVs) in P. aeruginosa. Killing kinetics of A NAg-passaged and B Ag+-passaged P. aeruginosa in comparison to the wild-type strain. The bacterium was first grown to early exponential phase and exposed to the silver antibacterials at their respective 1.5 × MIC dosages (4.5 µg/mL for NAg, 3 µg/mL for Ag+). The log10 decrease in cell population was determined relative to population at time 0 (as colony forming units). Refer to Additional file 1: Figure S3A, B for the biological replicate of the killing kinetics and to Additional file 1: Figure S3C, D for the two biological replicates of the killing kinetics of the strains isolated from the second biological replicate of the NAg and Ag+ passaging experiments. C Representative image of normal colonies of non-silver-treated wild-type, NAg-passaged and Ag+-passaged strains, D, E The colonies from the wild-type and NAg-passaged strains after 60 min exposure to NAg (at 1.5 × MIC dosage), F, G The colonies from the wild-type and Ag+-passaged strains after 60 min exposure to Ag+ (at 1.5 × MIC dosage). Note the occurrence of SCVs with the silver treatments. H, I The SCVs quantification in the silver-treated samples is presented as % relative to the total number of colonies and shown is the data from the two biological replicate of the NAg and Ag+ passaging experiments. *Indicates statistically significant higher occurrence of SCVs with p < 0.01 (**) and p < 0.001 (***), relative to the wild-type strain. The growth of normal colonies resumed upon sub-culturing of the SCVs from the (J) NAg-passaged and (K) Ag+-passaged strains, on antimicrobial-free medium