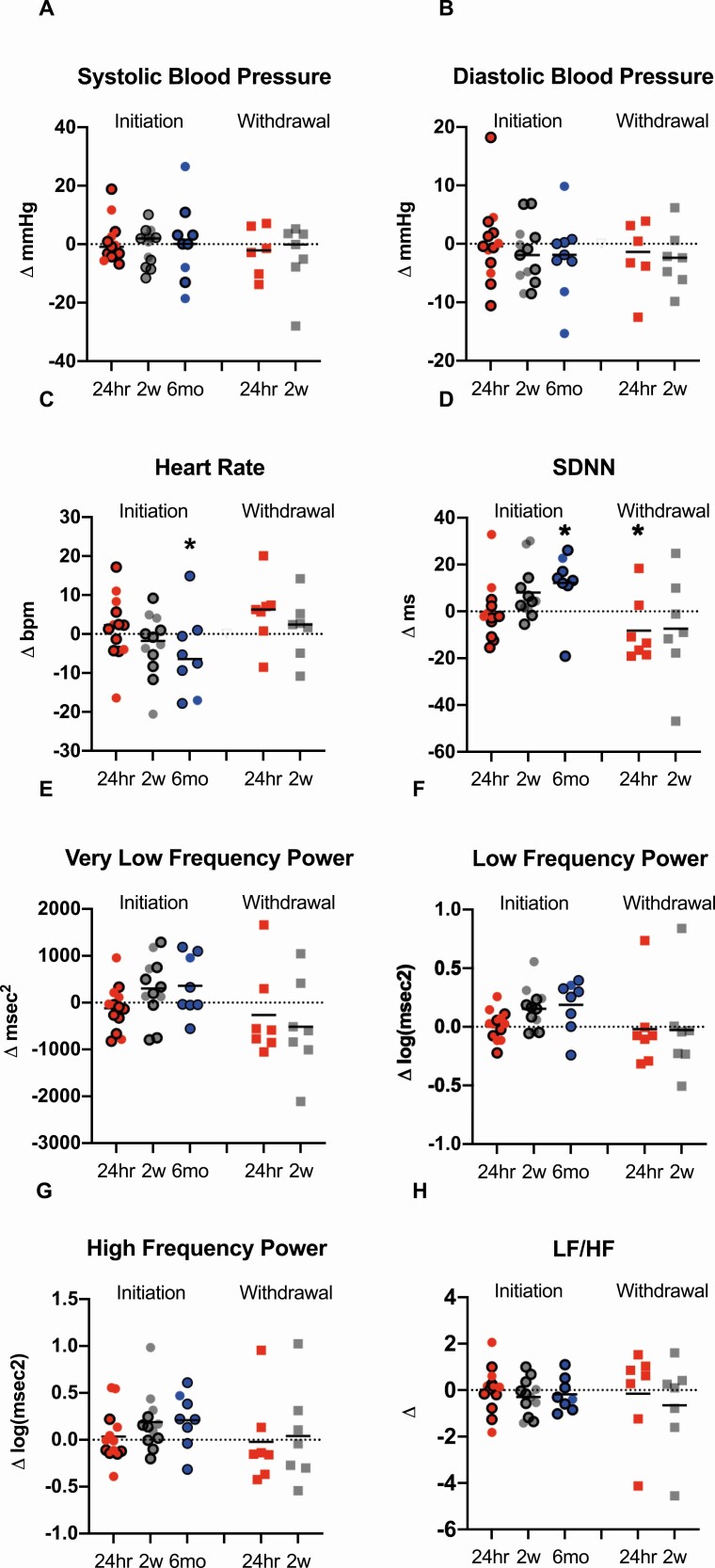
Figure 6.
Effects of metreleptin initiation or withdrawal on blood pressure and heart rate variability metrics in patients with lipodystrophy. Systolic blood pressure (A) and diastolic blood pressure (B) did not change from baseline to 24 h (24hr; red circles), 2 weeks (2w; gray circles) or 6 months (6mo; blue circles) after metreleptin administration or after 24 h (24hr; red squares) or 2 weeks (2w; gray squares) following metreleptin withdrawal. Heart rate (C) did not change from baseline to 24 h or 2 weeks after metreleptin initiation but decreased at 6 months. No changes in heart rate were observed at any time point following metreleptin withdrawal. (D) SD of the normal-to-normal distance (SDNN) increased (associated with decreased cardiovascular disease risk) after 6 months of metreleptin initiation and decreased (associated with increased cardiovascular disease risk) after 24 h of metreleptin withdrawal. (E) The very low frequency (VLF) component of heart rate variability, a measure of renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system effects on heart rate variability, (F) low frequency power component (LF), a measure of both sympathetic and parasympathetic influence on heart rate variability, and (G) high frequency power component (HF), a measure of parasympathetic impact on heart rate variability, did not change from baseline to 24 h, 2 weeks, or 6 months after metreleptin initiation or after 24 h and 2 weeks following metreleptin withdrawal. (H) The LF/HF ratio, a measure of sympathetic influence on heart rate variability, did not change at any time point following metreleptin administration or withdrawal. Patients with generalized lipodystrophy are shown as circles or squares without borders and those with partial lipodystrophy as circles with black borders. Comparisons were made using Wilcoxon rank-signed test and paired t-test for normally and nonnormally distributed data. Linear mixed effects models applying a Dunnett correction for multiple comparisons were used for outcomes measured at >2 time points. P < 0.05 represented statistical significance. P-values are 2-sided.