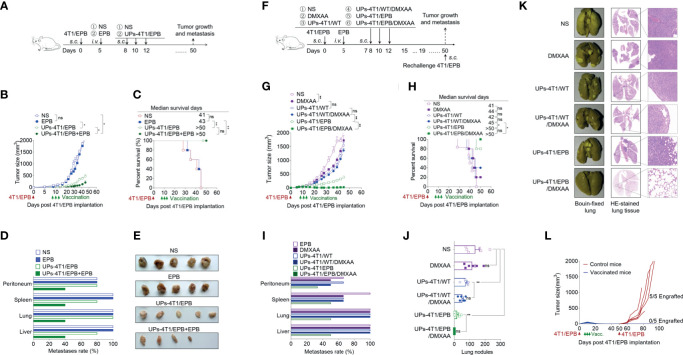
Figure 4.
Combination of ubiquitinated proteins (UPs)-4T1/epirubicin (EPB) nanovaccine with chemotherapy and stimulator of interferon genes (STING) agonists led to primary tumor regression and pulmonary metastasis eradication. (A) Immunization protocol of UP vaccination combined with chemotherapy. (B–E) The tumor growth (B) and survival (C) of mice (n = 5 to 6 per group) were monitored. Metastasis rate (D) and tumor photos (E) of tumor-bearing mice. (F) Immunization protocol of UP vaccination combined with chemotherapy and STING agonists. (G–L) The tumor growth (G), survival (H), and metastasis rate (I) of tumor-bearing mice (n = 6 per group) were monitored. Representative Bouin’s-fixed lungs and microscopic sections of lung tissues with HE stain (J). The pulmonary metastatic nodules of the lung tissue were counted (K). (L) The vaccinated mice that rejected the tumor following the combination therapy of UPs-4T1/EPB nanovaccine and 5,6-dimethylxanthenone-4-acetic acid treatment (five of the six treated mice) in (G) were rechallenged with 5 × 105 4T1/EPB tumor cells, and the tumor growth was monitored. P-values were determined by Mann–Whitney U-test. Kaplan–Meier survival curves were assessed by the log-rank Mantel–Cox test (C, H). The results are representative of three independent experiments, and data were expressed as means ± SEM (*p < 0.05; **p < 0.01; ns, not significant).