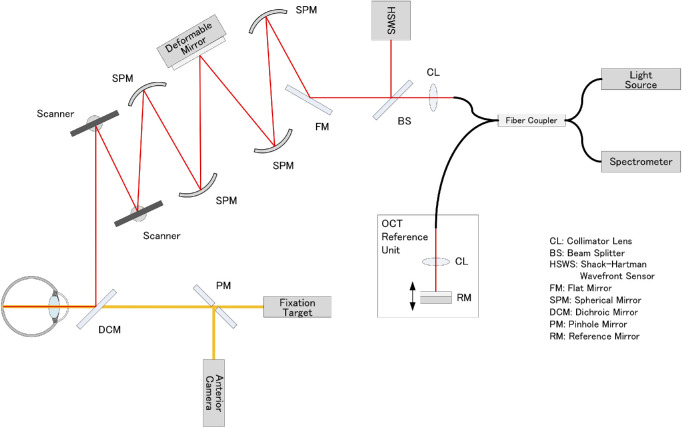
Figure 1.
Schematic representation of the optical structure of adaptive optics-optical coherence tomography. Collimated near-infrared light from a superluminescent diode light source propagates through the spherical mirrors, beam splitters, and dichroic mirror to the subject's eye. Two scanners are used to scan the imaging light two-dimensionally on the retina. A 97-actuator deformable mirror is used to compensate for the eye's aberration, which is measured using a Shack–Hartman wavefront sensor. The returning light from the retina is combined with the reference light, which is reflected by the reference mirror and detected by the spectrometer.