FIGURE 6.
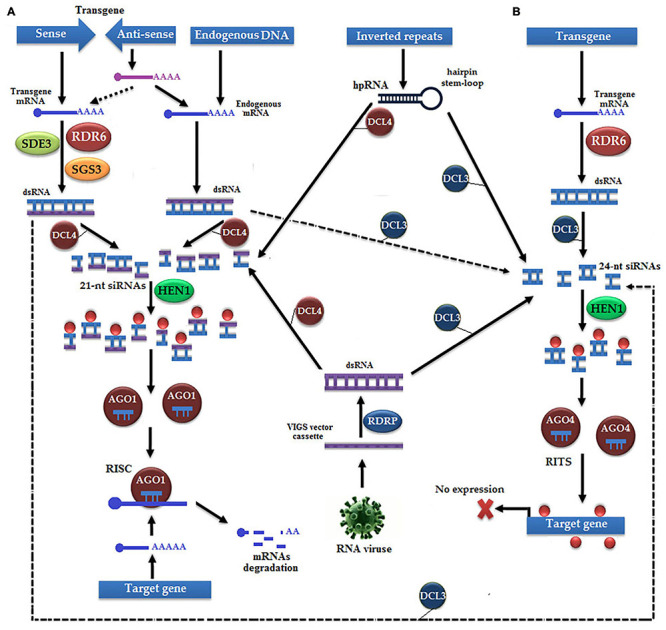
Transgene silencing occurs by the following two pathways: (A) post-transcriptional gene silencing (PTGS), which is initiated by sense or antisense transgenes, IR, hp-RNAs, and virus-induced gene silencing (VIGS). The sense strand is transcribed into mRNA, and transformed into dsRNA under the action of RDR6, suppressor of gene silencing 3 (SGS3), and RNA helicase (SDE3). Subsequently, dsRNA is either transformed into methylated 21-nt siRNAs by Dicer-like 4 (DCL4) and Hua Enhancer 1 (HEN1) or transformed into 24-nt siRNAs by AGO3 to cause gene silencing by the TGS pathway. The 21-nt siRNAs bind with AGO1 to make the RNA-induced gene silencing complex (RISC) that causes the degradation of mRNA of the target gene. Antisense strand is transcribed into mRNA, which either follows the same pathway with sense strand, or, like endogenous mRNA, transformed into dsRNA and bind with AGO to trigger the RISC. IR and VIGS follow either of the two available silencing pathways depending on the type of DCL. (B) TGS pathway, which is initiated with the transcription of transgene, dsRNA is formed under the action of RDR6, which is further cleaved into 24-nt siRNAs by DCL3, is methylated with HEN1, and make the RNA-induced transcriptional silencing (RITS) complex with the help of AGO4, which finally causes silencing.
