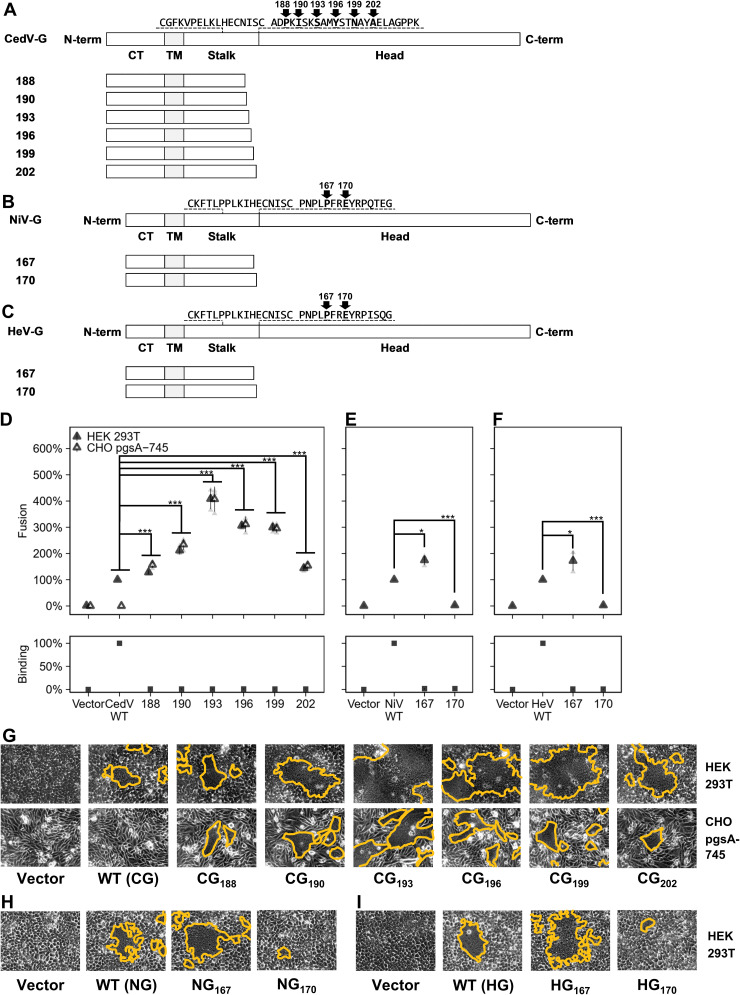
FIG 3.
A broad region of CedV G stalk induces robust cell-cell fusion. (A to C) Schematic representations of wild-type and headless CedV G, NiV G, and HeV G, respectively. Headless mutants were generated by mutating two downstream amino acids into stop codons and named after their C-terminal residues, as indicated. (D to F) Relative levels of fusion and ephrin B2 binding for wild-type or headless CedV G, NiV G, and HeV G, respectively, all normalized to their wild-type counterparts set at 100% (mean ± SD, n = 3). CedV G fusion was counted 18 to 22 hpt in HEK 293T cells (D, E, and F) and 22 to 26 hpt in CHO pgsA-745 cells (D). Fusion levels of CHO pgsA-745 cells were normalized based on the ratio of fusion for CG193 over wild-type CedV G in HEK 293T cells, to illustrate the fusogenicity of headless CedV G mutants. NiV G and HeV G fusion levels were measured at 12 to 14 hpt in HEK 293T cells. Different time points for CedV, NiV, and HeV fusion assays were chosen for optimal visualization of their respective fusion levels. (G to I) Representative fusion images (outlined in yellow) for CedV (G: 19 hpt for HEK 293T cells, 24 hpt for CHO pgsA-745 cells), or NiV and HeV (H and I: 13 hpt for HEK293T cells). Gray points in the plots represent individual data points.