E.D. Fig. 2: S1P increases in the dLN of BM chimeras after pIC injection.
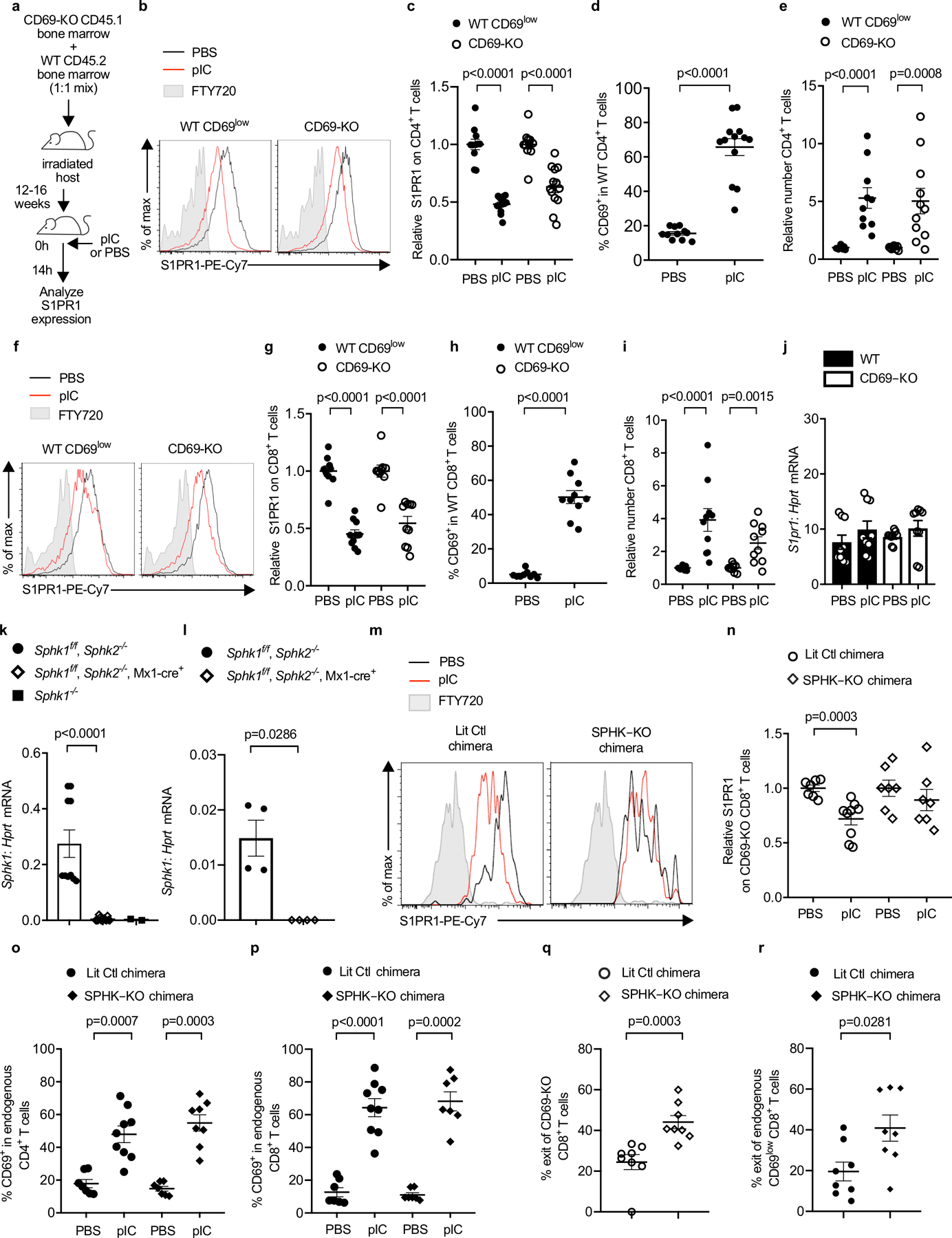
(a-j) C57BL/6 mice were lethally irradiated, reconstituted with a 1:1 mix of CD45.2+ WT and CD45.1+ CD69-KO BM, and allowed to recover for 12–16 weeks. The chimeras were injected s.c. with PBS or pIC, and dLN analyzed 14h later. Compilation of 3 (for CD8 analysis) - 4 (for CD4 analysis) experiments. (a) Experiment design. (b) S1PR1 on WT CD69low (left) and CD69-KO (right) CD4+ T cells. (c) Compilation. The S1PR1 MFI of the WT CD69low CD4+ T cells in each mouse was divided by the mean S1PR1 MFI of the WT CD69low CD4+ T cells in the PBS-treated group; the S1PR1 MFI of the CD69-KO CD4+ T cells in each mouse was similarly divided by the mean MFI of the CD69-KO CD4+ T cells in the PBS-treated group. Each point represents one mouse. PBS (n=11), pIC (n=13). (d) Percent CD69+ among WT CD4+ T cells. PBS (n=11), pIC (n=13). (e) Relative number of the indicated CD4+ T cells in the dLN. The number of CD4+ WT cells in the dLN of each mouse was divided by the mean number of CD4+ WT cells in the PBS-treated group; the number of CD69-KO CD4+ cells in each mouse was similarly divided by the mean number of CD69-KO CD4+ cells in the PBS-treated group. PBS (n=9), pIC (n=11). (f) S1PR1 expression on CD69low WT or CD69-KO CD8+ T cells. (g) Compilation, as in (c). PBS (n=9), pIC (n=10). (h) Percent CD69+ among WT CD8+ T cells. PBS (n=9), pIC (n=10). (i) Relative number of the indicated CD8+ T cells, as in (e). PBS (n=9), pIC (n=10). (j) RT-qPCR for S1pr1, normalized to Hprt. Compilation of 3 experiments. PBS (n=9), pIC (n=9). (k) RT-qPCR for Sphk1 in bone marrow of pIC-treated Sphk1f/fSphk2−/− (n=5 animals, bone marrow cells split into 2 samples prior to RNA purification), pIC-treated Sphk1f/fSphk2−/−Mx1-Cre+ (n=7 animals, bone marrow cells split into 2 samples prior to RNA purification), and Sphk1−/− (n=2 animals). Compilation of 2 experiments. (l) RT-qPCR for Sphk1 in blood of pIC-treated Sphk1f/fSphk2−/− (n=4) and pIC-treated Sphk1f/fSphk2−/−Mx1-Cre+(n=4) animals. One experiment. (m-r) UBC-GFP+ mice were lethally irradiated, reconstituted with pIC-treated Sphk1f/f Sphk2−/− Mx1-Cre+ CD45.2+ (SPHK-KO) or littermate control (LitCtl) BM, and left to recover for 12–14 weeks. Chimeras received CD45.1+ CD69-KO T cells i.v. 24h later, chimeras were injected s.c. with pIC or PBS. 14h later, dLN were analyzed. (m) S1PR1 on CD69-KO CD8+ T cells in LitCtl chimeras (left) or SPHK-KO chimeras (right). FT720-treated mouse served as a negative control. (n) Compilation of 3 experiments. The S1PR1 MFI on the CD69-KO CD8+ T cells in each mouse was divided by the mean S1PR1 MFI on the CD69-KO CD8+ T cells in the PBS-treated group. LitCtl (PBS n=7, pIC n=9); SPHK-KO (PBS n=7, pIC n=7). (o) Percent CD69+ among CD4+ T cells. Compilation of 3 experiments. LitCtl (PBS n=7, pIC n=9); SPHK-KO (PBS n=7, pIC n=8). (p) Percent CD69+ among CD8+ T cells. Compilation of 3 experiments. LitCtl (PBS n=7, pIC n=9); SPHK-KO (PBS n=7, pIC n=7). (q,r) CD69-KO CD45.1+ lymphocytes were transferred into LitCtl or SPHK-KO BM chimeras. 24h later, the chimeras were injected s.c. with pIC. 14h later, half of the mice in each group were euthanized and the cells in the dLN were counted. The remaining mice were injected i.v. with anti-αL and anti-α4 neutralizing antibodies. These antibodies blocked any further lymphocyte entry into the LN. 4h later, these mice were euthanized and the cells in the dLN were counted. The decline in cell numbers in the LN over 4 hours, with no further cell entry, indicated the exit rate. Compilation of 3 experiments. SPHK-KO (t=0 n=8; t=4h n=8), LitCtl (t=0 n=6, t=4h n=8). (q) Percent exit of CD69-KO CD8+ T cells. (r) Percent exit of endogenous CD69low CD8+ T cells. Each point represents one mouse at t=4h relative to the average at t=0. Data presented as mean values +/− SEM. Mann-Whitney two-tailed t test.
