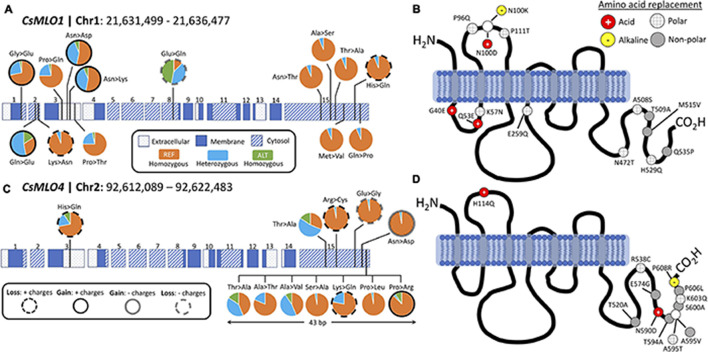
FIGURE 6.
Protein structure and polymorphism analysis of the two clade V genes (CsMLO1 and CsMLO4) in 32 distinct cannabis cultivars aligned against the CBDRx reference genome. Panels A and B exhibit all non-synonymous nucleic acid substitutions (A) and amino acid replacements (B) identified in CsMLO1 (located on chromosome 1) from 32 hemp and drug-type cannabis cultivars. Panels (C,D) exhibit all non-synonymous nucleic acid substitutions (C) and amino acid replacements (D) identified in CsMLO4 (located on chromosome 2) from the same 32 hemp and drug-type cannabis cultivars as shown on panels (A,B). On panels (A,C) (gDNA), pie charts display, for each SNP along the coding sequence, the genotype frequencies calculated among the 32 cultivars. Colored horizontal rectangles on panels (A,C) represent the exons, numbered from 1 to 15: dotted rectangles represent extracellular domains of the resulting protein, while blue and striped rectangles represent membrane and cytoplasmic domains, respectively. Genotype frequency color code on panels (A,C): samples called as homozygous for the reference allele are depicted in orange, samples called as heterozygous are depicted in light blue, and samples called as homozygous for the alternate allele are depicted in green. On panels (B,D) (amino acid sequence), the gray vertical rectangles depict transmembrane domains and the solid black curves depict cytoplasmic and extracellular loops. Resulting amino acid replacements on panels (B,D) are color-coded according to the gain or loss of polarity: red circles with white cross display a replacement with an acidic amino acid, yellow circles with black hyphen represent a replacement with an alkaline amino acid, gray circles display a replacement with a non-polar amino acid, and gray-striped white circles represent a replacement with a polar amino-acid.