Figure 6. Intrathecal (IT) interleukin-1 receptor antagonist (IL-1ra) administered either 15 days (Panels A,B) or 29 days (Panels C,D) after intradermal myelin oligodendrocyte glycoprotein (MOG), reverses EAE-related pain in male Dark Agouti rats.
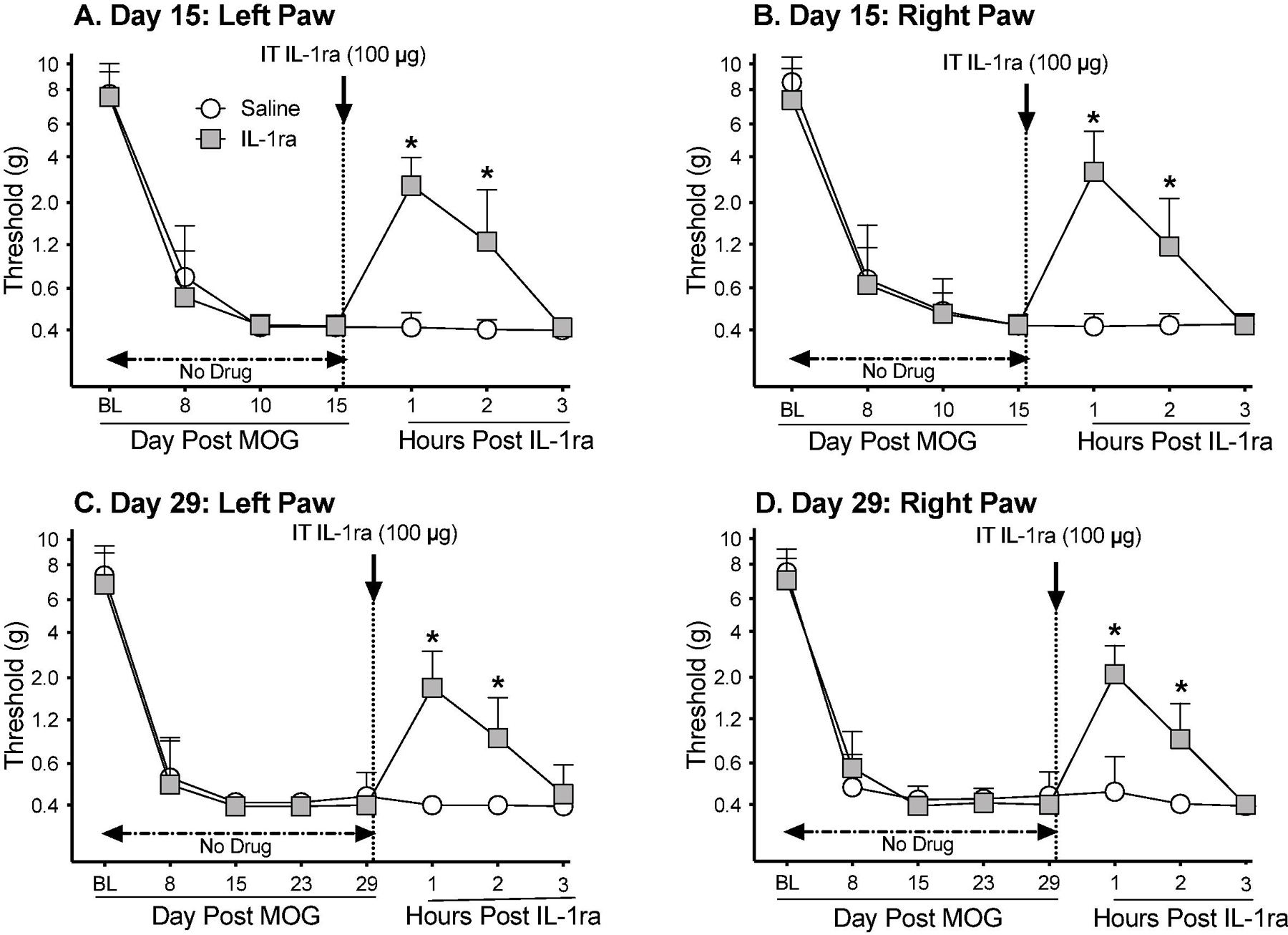
Male Dark Agouti rats were baselined (BL) for low-threshold mechanical withdrawal thresholds via the von Frey test, followed by intra-dermal low-dose (4 µg) myelin oligodendrocyte glycoprotein (MOG). Allodynia was assessed thereafter across the timecourse shown. IT IL-1ra (100 µg) vs. saline was administered either on Day 15 or Day 29 post-MOG. Panels A and B: IL-1ra reversed allodynia when administered Day 15 post-MOG, relative to saline control (main effect of drug: left paw: F(1,13) =72.96, p<0.0001; right paw: F(1,13) =12.21, p<0.005). Panels C and D: IL-1ra also reversed allodynia when administered Day 29 post-MOG, relative to saline control (main effect of drug: left paw: F(1,12) =148, p<0.0001; right paw: F(1,12) =50.38, p<0.0001).
