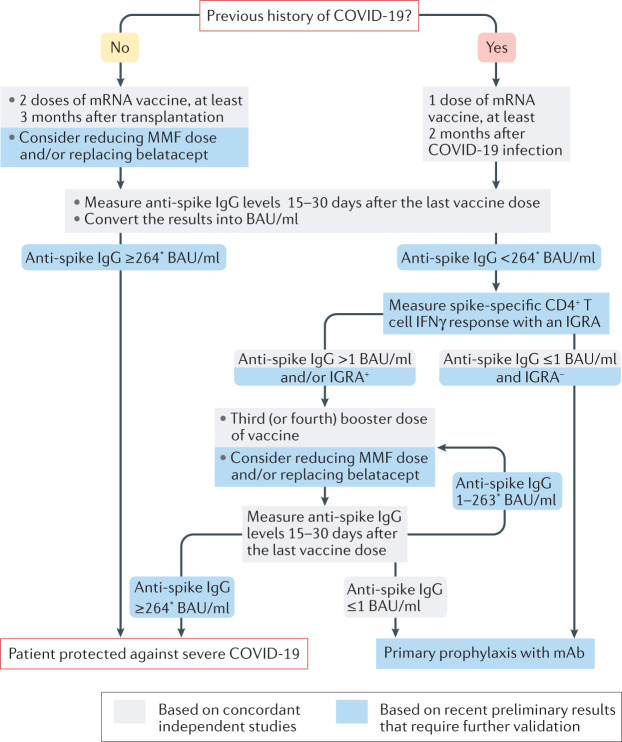
Fig. 1. Suggested vaccination approach for protection against COVID-19 in kidney transplant recipients.
The presence of SARS-CoV-2-neutralizing antibodies and vaccine efficacy against primary symptomatic COVID-19 correlates well with anti-spike protein IgG titres, which can be measured with commercial serological tests4. Another advantage of these antigen-binding assays is that their results can be converted to the WHO international standard (NIBSC code 20/136) and expressed in binding antibody units (BAU)/ml, making individual results comparable across different platforms and laboratories. Most reports suggest that the antibody response peaks 15 days after the last dose of vaccine and remains stable until at least day 30. Follicular helper CD4+ T (TFH) cells seem to be instrumental for the differentiation of spike-specific B cells into antibody-producing plasma cells. However, enumeration of spike-specific TFH cells in the circulation of patients requires complex techniques that are not available in routine clinical practice. We have demonstrated in a preprint study that IFNγ levels measured with commercially available IFNγ release assays (IGRAs) performed within 30 days after the last dose of vaccine correlate with the number of spike-specific TFH cells8. mAb, monoclonal antibodies; MMF, mycophenolate mofetil. *This threshold was defined in one preprint publication only and may vary according to the virus variants and the neutralization tests used.