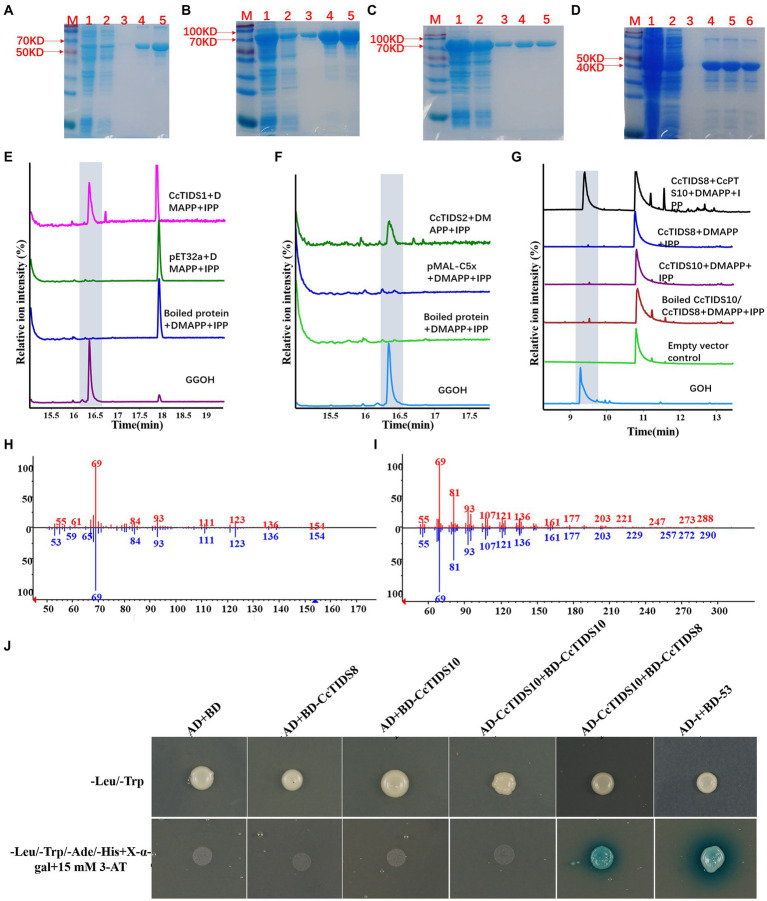
Figure 8.
Gas chromatography–mass spectrometry profile showing in vitro reaction products of C. camphora trans-prenyltransferases CcTIDS1, CcTIDS2, CcTIDS8, and CcTIDS9, where different prenyldiphosphates were used as substrates. Expression and purification of (A) CcTIDS1, (B) CcTIDS2, (C) CcTIDS8, and (D) CcTIDS10 recombinant protein from E. coli Rosetta (DE3) harboring pET32a(+)–CcTIDS1/CcTIDS10 or pMAL-C5x–CcTIDS2/CcTIDS8, where lane 1 shows the total protein after induction, 2 shows the soluble protein, 3–6 show the purified CcTIDS1 or CcTIDS2, CcTIDS8, or CcTIDS10 recombinant protein from the first to the fourth collected tube. The GC–MS chromatogram of the reaction products generated by (E) CcTIDS8 and CcTIDS10, (F) CcTIDS1, and (G) CcPTS2 and the acid hydrolysis products of geraniol (GOH) and gerylgeraniol (GGOH) standards. (H) Mass spectra of GOH standard (red) and products in the NIST14/Wiley275 library (blue). (I) Mass spectra of the GGOH standard (red) and products in the NIST14/Wiley275 library (blue). (J) Confirmation of the interaction between CcTIDS8 and CcTIDS10 using a yeast two-hybrid system, where blue color indicates an interaction. Yeast cells harboring both constructs were spotted on synthetic dropout (SD) medium lacking Ade, His, Leu, and Trp (SD/−4) to test for protein interactions. AD: pGADT7; BD: pGBDT7; AD-T: pGADT7::T; BD-53: pGBKT7-53. Cells co-transformed with pGADT7::T and pGBKT7-53 were included as a positive control, and pGADT7 and pGBDT7 as a vector control.