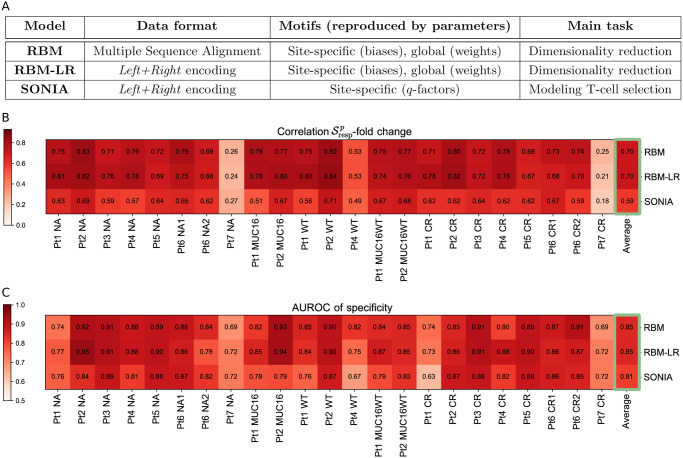
Fig 8. Comparison of the methods.
A: Schematic summary of the characteristics of the three sequence-based probabilistic modeling approaches used: RBM, RBM-LR, SONIA. B-C: Summary of the results we obtained for the samples from [16] using the approaches in A, in particular the correlation between the model’s response score and TRB clone fold change when retaining the 125 most abundant clones (B) and the AUROC-based measure of response specificity (C). Both these measures highlight a different degree of specific response to the stimulation, that overall stays high across the samples apart from Pt7, where response to the peptides tested was rather unspecific. For each sample, the results from the three methods are well in agreement (see also Figs 3C and 4E). High values of the AUROC and of the -fold change correlation reflect also how well the probability inferred by each method reproduces the clone abundance (see S3 Fig, Materials and methods), thus we report the averages over all samples (last column) for a comparison of the methods’ performance. This comparison shows that the general performance is higher for RBM-based approaches than for SONIA and is the same for RBM and RBM-LR.