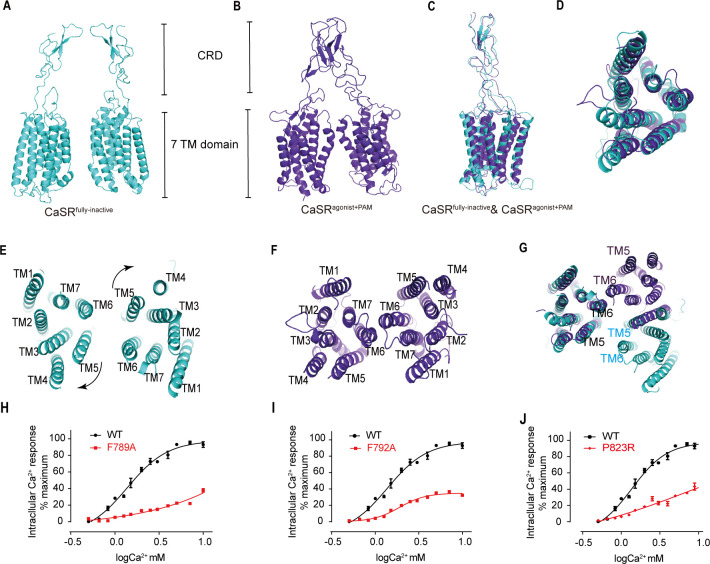
Figure 7. The closure of VFT leading to the rearrangement of inter-7TMDs.
(A) Front view of CaSRfully inactive CRDs and 7TMDs (cyan). (B) Front view of CaSRagonist+PAM CRDs and 7TMDs (purple). (C) The alignment of the part of CRD and 7TMDs in both fully inactive and agonist+PAM bound CaSR. (D) The alignment of inactive and agonist+PAM bound 7TMDs from top view. (E–G) The 7TMDs interface in the fully inactive state of CaSR is mediated by TM5 and TM6 (cyan) from top view and that of the agonist+PAM state is driven by TM6 from top view. Superposition of 7TMD of the inactive (cyan) and agonist+PAM bound CaSR (purple) show the rotation of 7TMDs. (H–J) Dose-dependent intracellular Ca2+ mobilization expressing WT (black dots) and mutant (red dots) CaSR (Figure 7—source data 1). The single mutations of F789A (H), F792A (I), and P823R (J) were designed based on the inactive density map. For (H–J), N = 4, data represent mean ± SEM.