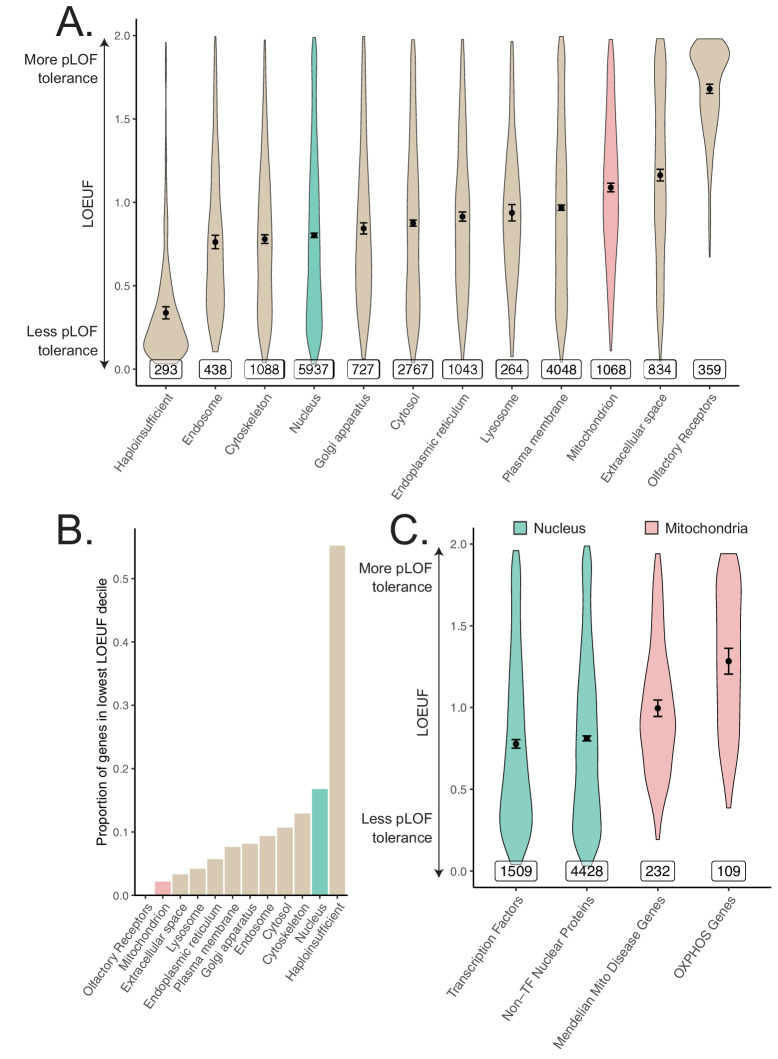
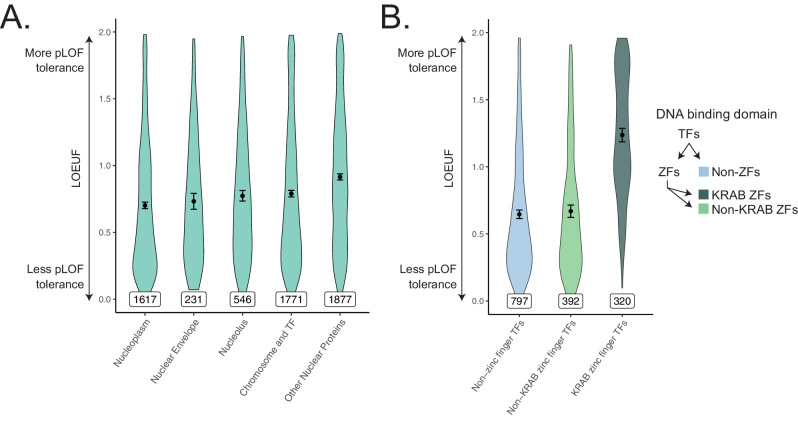
Figure 5. Differences in constraint distribution across organelles.
(A) Constraint as measured by LOEUF from gnomAD v2.1.1 for genes comprising organellar proteomes, book-ended by distributions for known haploinsufficient genes as well as olfactory receptors. Lower values indicate genes exacting a greater organismal fitness cost from a heterozygous LoF variant (greater constraint). (B) Proportion of each gene-set found in the lowest LOEUF decile. Higher values indicate gene-sets containing more highly constrained genes. (C) Constraint distributions for subsets of the nuclear-encoded mitochondrial proteome (red) and subsets of the nucleus (teal). Black points represent the mean with 95% CI. Inset numbers represent gene-set size.