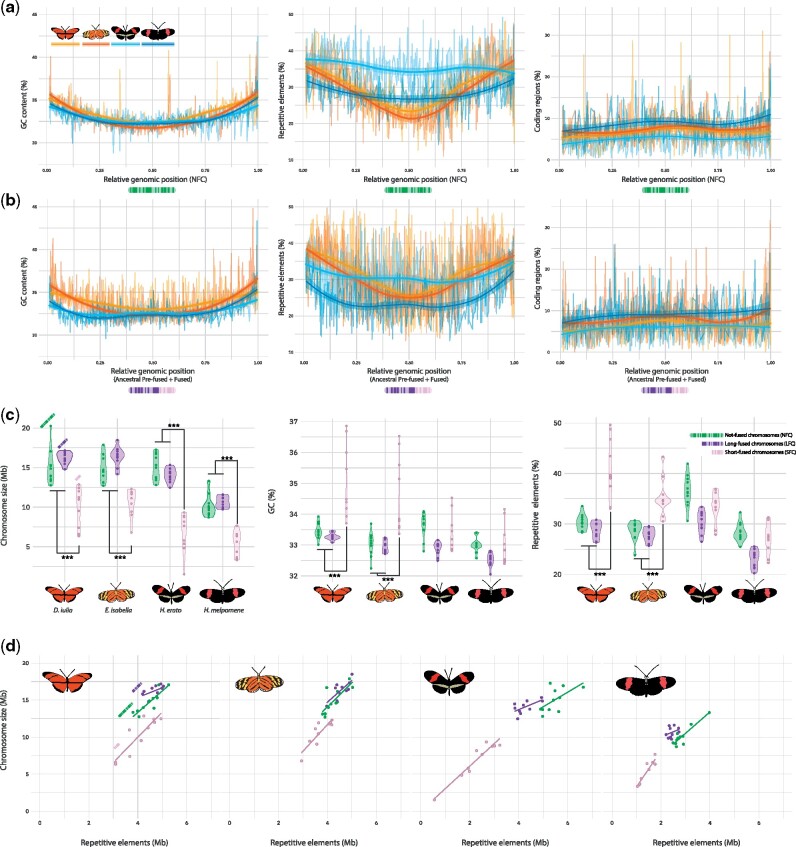
Fig. 2.
(a) GC content (%), repeat content (%) and coding density within 100 kb nonoverlapping windows in not fused chromosomes (NFC) of the four species (showed in color). (b) Same as (a) but for Heliconius fused chromosomes and their homologous in Dryas iulia and Eueides isabella. In both cases, GC and repeat distributions are accumulating at the chromosome tails, whereas coding density seems to be slightly denser in the central part of chromosomes. For fused chromosomes in Heliconius spp. fusion points is placed at 0.5 of the x-axis. (c) Violin plots of the different chromosome types, showing how and where size, CG content (%) and repetitive elements (%) are different. Short-fused chromosomes (SFC) appear to be smaller and with higher GC and repeat content compared with not-fused (NFC) and long-fused (LFC) chromosomes, which, in turn, to not appear significantly different. ***Wilcoxon rank-sum test “less”; P values <0.001. (d) Scatter plots between chromosome size and their repetitive element (Mb), their relative regression line, for the different chromosome types (color) for each species.