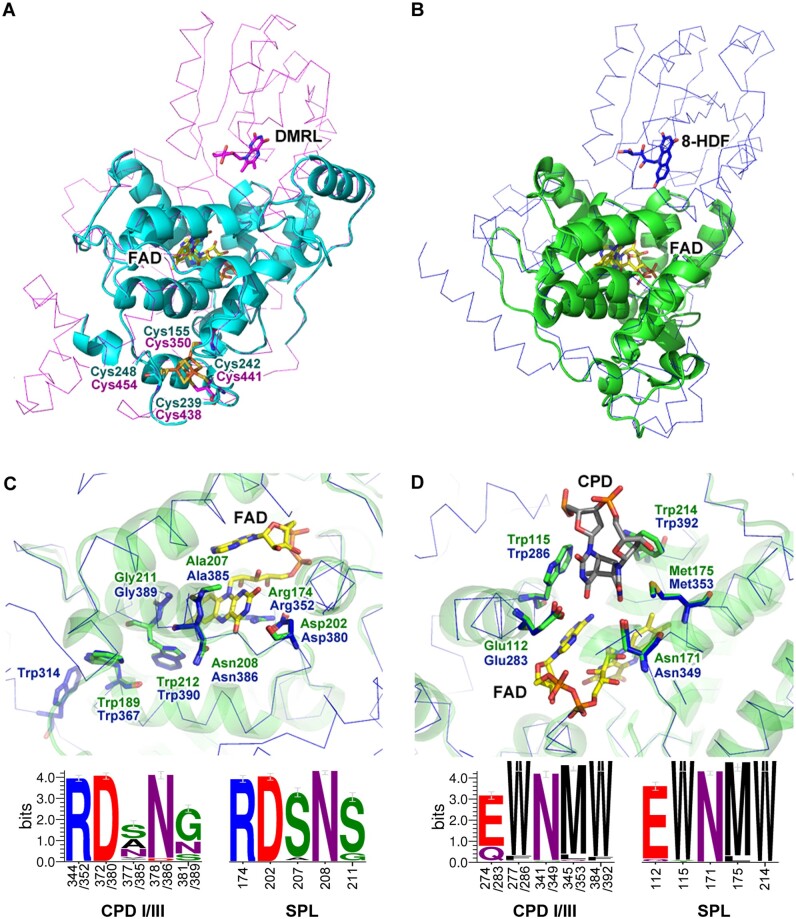
Fig. 3.
The modeled structures of RfSPL were shown in (A) cyan and (B) green cartoon representations which were constructed using the crystal structure of Agrobacterium fabrum FeS-BCP (AfPhrB, PDB ID: 4DJA, magenta ribbon) and that of Synechococcus elongatus class I CPD photolyase (SeCPDI, PDB ID: 1TEZ, blue ribbon) as the template, respectively. (C) and (D) were the detailed views of the putative FAD- and substrate-binding pockets of RfSPL modeled on the crystal structure of SeCPDI. The lower parts of (C) and (D) were the WebLogo presentations of the FAD- and substrate-binding sites of 221 class I/III CPD photolyases and those of 191 SPLs, respectively. The numbers under the abscissae indicated the residue numbers of EcCPDI/SeCPDI and RfSPL, respectively. The FAD, DMRL, and 8-HDF cofactors, the iron–sulfur cluster in the templates, the putative CPD substrate, and the key residues in the templates and the modeled structures were shown in the stick representations.