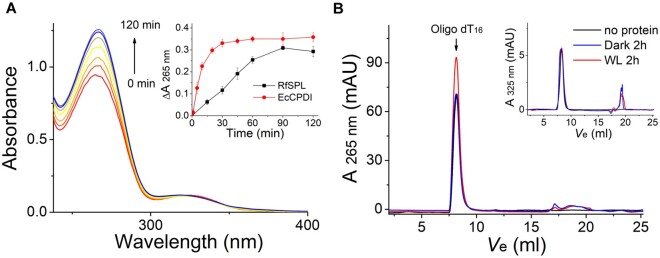
Fig. 5.
RfSPL is a CPD photolyase. The assay mixture contained 0.1 mg/ml Escherichia coli expressed RfSPL protein (with ∼0.1 µM binding FAD), 10 µM UV-oligo(dT)16, and 1 mM DTT in Protein buffer at pH 6.0. The mixture was illuminated under a white-light LED (irradiance of ∼800 W m−2). (A) The time-dependent absorption spectra of the assay mixture. In the inset, the change of absorbance at 265 nm versus time was shown. An activity assay result of EcCPDI under similar conditions was also shown to give a reference. (B) The assay mixture was boiling and centrifugation after illumination for 2 h, and the supernatant was analyzed by size exclusion chromatography (red line, WL 2 h). The elution profile of a control that illuminated in the absence of the RfSPL protein was shown in a black line (no protein), and that of a control kept in the dark for 2 h was shown in a blue line (dark 2 h). The elution peak of the oligo(dT)16 substrate was indicated by an arrow. The restoration of absorption at 265 nm was indicative of the conversion of CPDs to pyrimidines. The elution profiles detected at 325 nm were shown in the inset. The absorption at 325 nm of the substrate peaks was almost unchanged before and after illumination.