Fig. 6 |. Maximum activation of Dcp1/Dcp2ext in condensates requires Edc3.
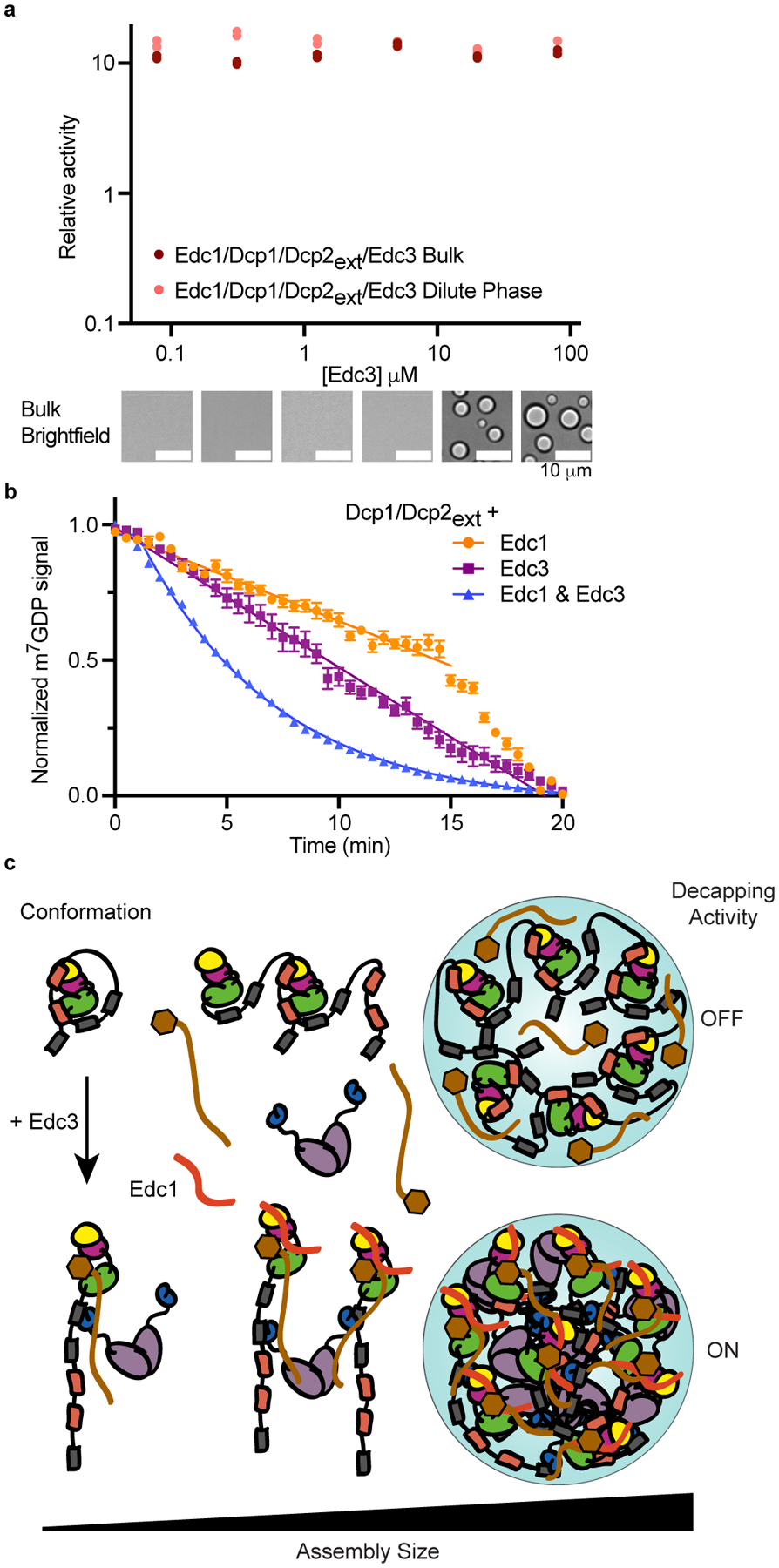
a, Edc1 activates Dcp1/Dcp2ext independent of Edc3-mediated phase separation and abrogates contribution of decapping in condensates. Data from two independent experiments are shown and relative activity reflects ratio between observed rates and rates for Dcp1/Dcp2ext in absence of Edc1 and Edc3. Representative micrographs are from three independent experiments with similar results. b, Edc1 activates Dcp1/Dcp2ext in droplets but requires Edc3 for maximal activation. Data represents mean ± s.e.m from twenty droplets examined over two independent experiments. c, Model showing how Edc3 mediates a conformational change in Dcp1/Dcp2 that is coupled to an alteration of the protein-protein interactions promoting higher-order assemblies found in condensates. These changes in interactions switch decapping activity from an off to on state. Edc1 stabilizes the active conformation to activate Dcp1/Dcp2 inside and outside condensates.
