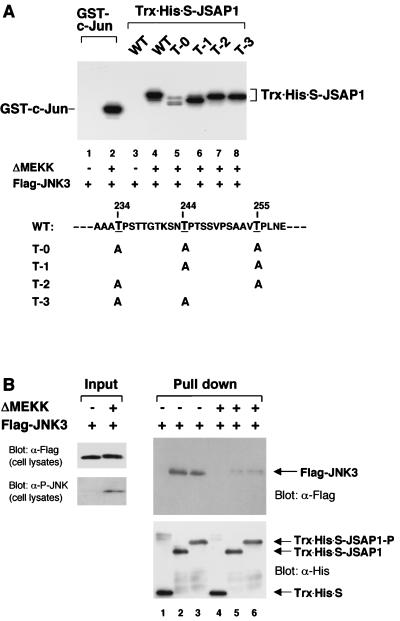
FIG. 3.
Phosphorylation of JSAP1 by JNK3 (A) and its effect on the interaction with JNK3 (B). (A) COS-7 cells were transiently transfected with 1.5 μg of pFlag-CMV2-JNK3 with or without 0.05 μg of pEF-3XHA-ΔMEKK. Cell lysates were immunoprecipitated with anti-Flag antibody, and the in vitro kinase assay was carried out as described in Materials and Methods. GST–c-Jun (residues 1 to 79) and Trx-His-S-JSAP1 (residues 115 to 274) were used as substrates. The mutants of JSAP1 (T-0, T-1, T-2, and T-3) were as indicated. WT, wild type. The concentration of each substrate was 1 pmol/μl in 30 μl of total volume. (B) COS-7 cells were transiently transfected with 1.5 μg of pFlag-CMV2-JNK3 with or without 0.05 μg of pEF-3XHA-ΔMEKK. The unstimulated (lanes 1 to 3) and stimulated (lanes 4 to 6) Flag-JNK3 were precipitated from cell lysates with 0.5 μg of immobilized Trx-His-S protein (lanes 1 and 4) or the unphosphorylated (lanes 2 and 5) or phosphorylated (lanes 3 and 6) Trx-His-S-JSAP1 and analyzed by immunoblotting with anti-Flag or anti-His antibody. Expression of Flag-JNK3 was examined by immunoblotting 1/10 of the cell lysates used in the binding reactions. The phosphorylated form of Flag-JNK3 was detected with a phospho-specific JNK (P-JNK) antibody.