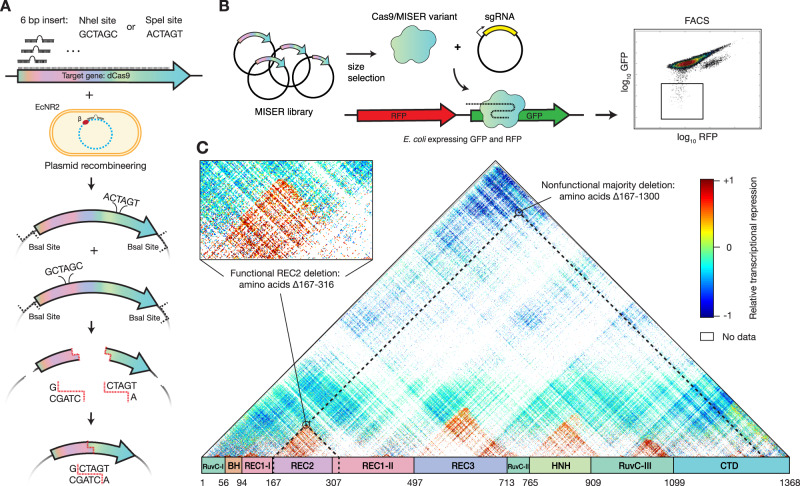
Fig. 1. Minimization by iterative size exclusion and recombination (MISER).
A MISER library construction. A 6-bp SpeI or NheI recognition site is inserted separately into a dCas9-encoding plasmid flanked by BsaI sites using plasmid recombineering. The resultant libraries are digested with BsaI and either SpeI or NheI, and the two fragment pools are combined and ligated together to generate a library of dCas9 ORFs possessing all possible deletions. B The MISER library is cloned into a vector and co-transformed in E. coli expressing RFP and GFP with a sgRNA targeting GFP. The library products are expressed, functional variants bind to the target, and repress the fluorophore. Repression activity in vivo is measured by flow cytometry. C Enrichment map of the MISER deletion landscape of S. pyogenes dCas9. A single pixel within the map represents an individual variant that contains a deletion beginning where it intersects with the horizontal axis moving to the left (N) and ends where it intersects with the axis moving to the right (C). Larger deletions are at the top, with some deletions almost spanning the whole protein. The heatmap shows relative repression activity of variants from two FACS sorts of a single replicate. The map is a composite of Slice 4 and Slice 5 in Supplementary Fig. 3A, B, which present variant ratios post- versus pre-FACS sorting.