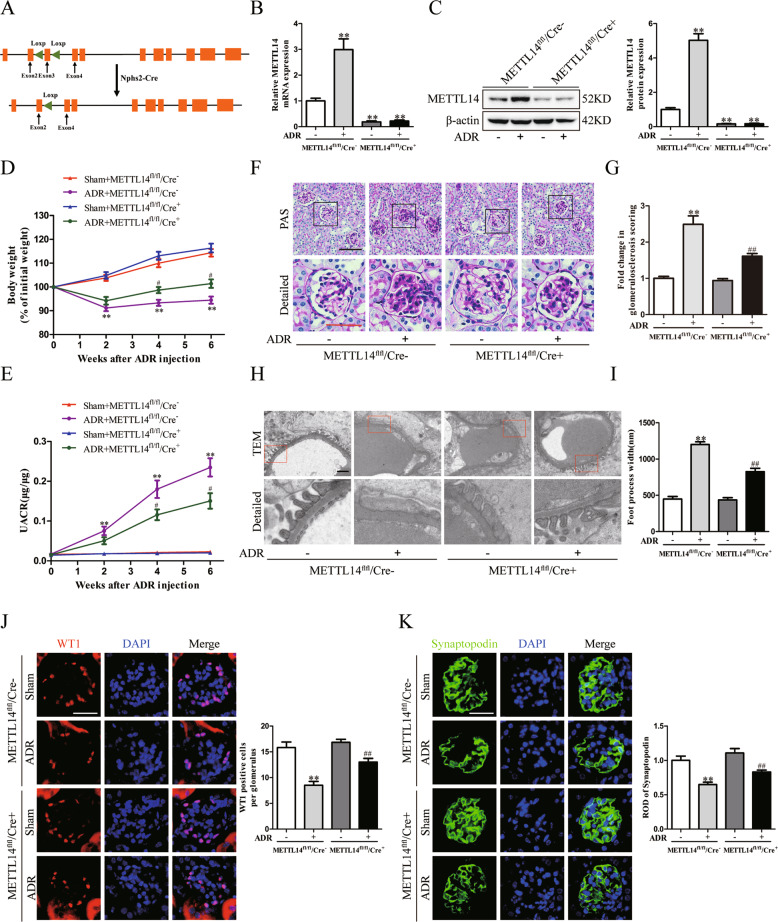
Fig. 3. Podocyte-selective deletion of METTL14 alleviated ADR-induced glomerular injury in vivo.
Wild-type (METTL14fl/fl/Cre−) mice and podocyte-specific METTL14 knockout (METTL14fl/fl/Cre+) mice were injected with saline or ADR (19.5 mg/kg). A The diagram depicting generation of METTL14fl/fl/Cre+ mice. Exon 3 of METTL14 gene were deleted in podocytes using Cre–LoxP recombination system. B The relative mRNA levels of METTL14 in isolated glomeruli from different groups of mice (n = 4). C Representative immunoblots and quantitative analysis showing the evident decreased protein levels of METTL14 in isolated glomeruli from METTL14fl/fl/Cre+ mice with ADR injection (n = 4). D Quantitative analysis of body weight in different groups of mice (n = 6). E UACR (urine albumin-to creatinine ratio) in each group (n = 6). F Representative images of PAS staining on kidney sections in different groups of mice. Scale bar: black 40 μm, red 20 μm. G Assessment of morphologic injury quantified with messangial matrix expansion in each group (n = 6). H Representative transmission electron microscopy images of podocyte foot process in different groups of mice. Scale bar, 1 μm. I Quantitative analysis of podocyte foot process effacement and GBM thickness in the four groups (n = 6). J Representative images and quantification of immunofluorescence staining for WT1 on kidneys of each group. Scale bar, 20 μm (n = 6). K Representative images and quantification of immunofluorescence staining for synaptopodin on kidneys of each group. Scale bar, 20 μm (n = 6). **P < 0.01 vs. METTL14fl/fl/Cre− mice injected with saline, #P < 0.05, ##P < 0.01 vs. METTL14fl/fl/Cre− mice with ADR injection. Data are presented as mean ± SEM.