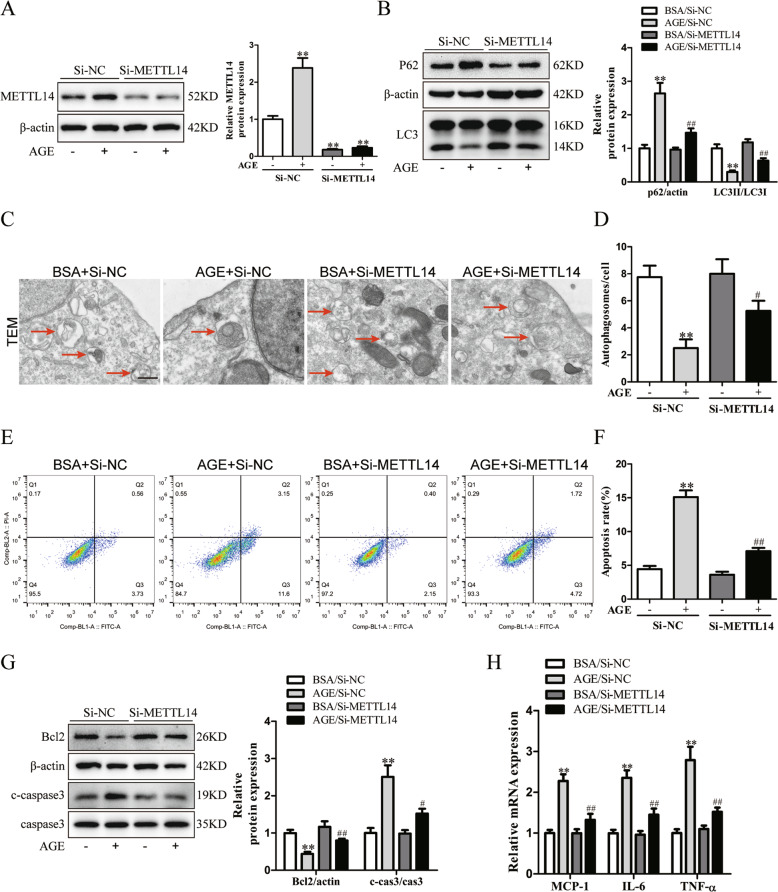
Fig. 6. Gene silencing of METTL14 protected against AGE-induced podocyte injury in vitro.
Podocytes transfected with negative SiRNA (SiNC) or METTL14 knockdown SiRNA (SiMETTL14) were administrated with BSA or AGE (50 μg/ml). A Representative immunoblots and quantitative analysis of METTL14 in different groups of podocytes (n = 6). B Western blot analysis showing METTL14 knockdown weakened AGE-induced inhibition of P62 degradation and LC3-I to LC-3II conversion in podocytes (n = 6). C, D Representative electronic micrographs and quantitative analysis showing METTL14 silencing ameliorated the reduction of typical autophagosomes in podocytes induced by AGE treatment. Scale bar, 500 nm (n = 4). E, F Apoptosis of podocytes with different treatments analyzed by flow cytometry. The results showed that METTL14 knockdown downregulated the percentage of apoptotic podocytes in AGE-treated podocytes (n = 6). G Western blot analysis of apoptosis-related proteins (Bcl2 and cleaved caspase3) in podocytes with different treatment (n = 6). H Quantitative RT-PCR analysis showing the reduction of inflammatory cytokines (MCP-1, IL-6 and TNF-α) mRNA levels with METTL14 inhibition in AGE-treated podocytes (n = 6). **P < 0.01 vs. BSA + SiNC group, #P < 0.05, ##P < 0.01 vs. AGE + SiNC group. Data are presented as mean ± SEM.