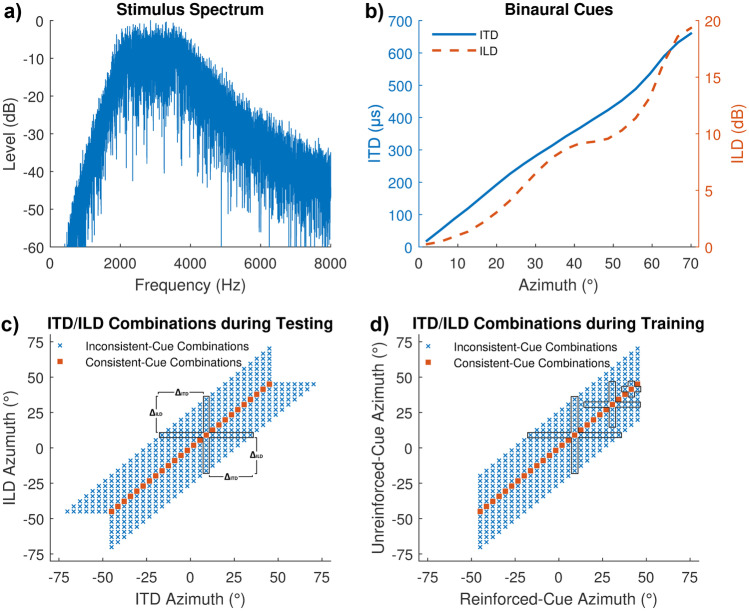
Fig. 2.
Experimental setup and stimuli. a Spectrum of the auditory stimuli used. b Functional relation between the azimuth and the binaural cues as derived by Xie (2013) from the KEMAR head-related impulse responses (HRIRs), with ITDs (solid line) referring to the left ordinate and ILDs (dashed line) referring to the right ordinate. ITDs are based on broadband cross-correlation of the left and right ear HRIRs. ILDs are based on HRTF magnitudes at 2.8 kHz. c ITD/ILD-azimuth combinations used in the pre- and posttest. The frame indicates the azimuthal offsets ΔITD and ΔILD that were used to estimate the parameters of the regression analysis for the pre-/posttest data at one example azimuth (9°). d All cue combinations used in the training. For the ITD group, reinforced and unreinforced cues were ITD and ILD, respectively, and for the ILD group, reinforced and unreinforced cues were ILD and ITD, respectively. The frames indicate the data that were used to estimate the parameters of the regression analysis for the training data at example azimuths of 9° (large frame), 30.6° (medium frame), and 41.4° (small frame). The reduction of frame size towards the edge was required to ensure symmetric distributions (see text)