Figure 1. STING N153S gain-of-function bone-marrow-derived macrophages (BMDMs) are hyper-responsive to cyclic di-GMP, a bacterial cyclic dinucleotide.
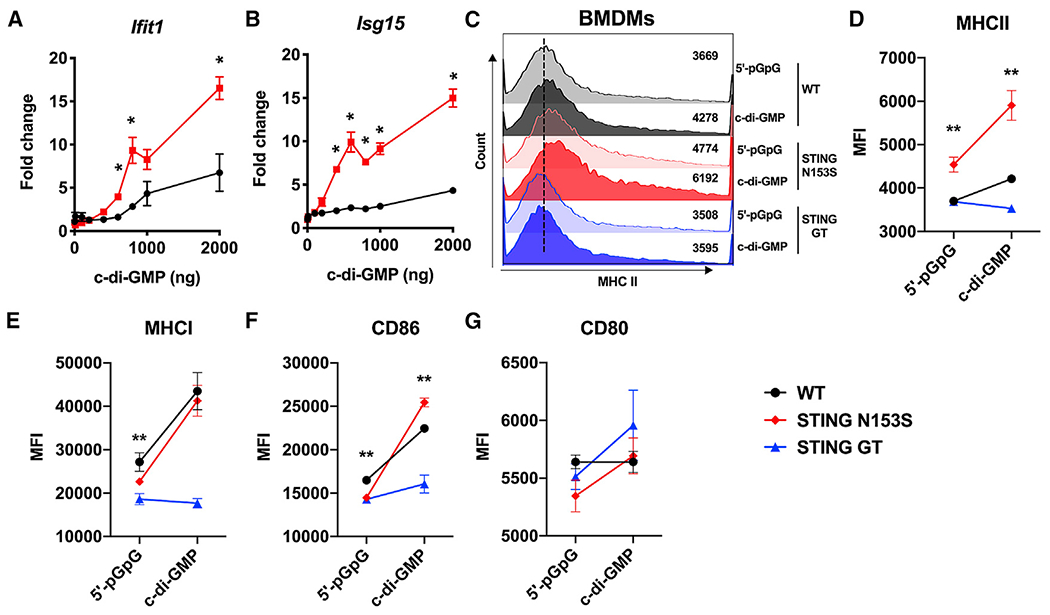
BMDMs were isolated from WT, STING N153S (SAVI), or STING Goldenticket mice following stimulation with cyclic di-GMP or control.
(A and B) Gene expression levels of IFIT1 and ISG15 were measured in WT and STING N153S BMDMs.
(C–G) Geometric mean of (C and D) MHC class II, (E) MHC class I, (F) CD86, and (G) CD80 on WT, STING N153S, or STING Goldenticket mice was measured by flow cytometry following stimulation with cyclic di-GMP or control.
Data represent the mean ± SEM of 4 biological replicates per group, which were pooled from 2 independent experiments. Results were analyzed by Mann-Whitney test. *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01.
