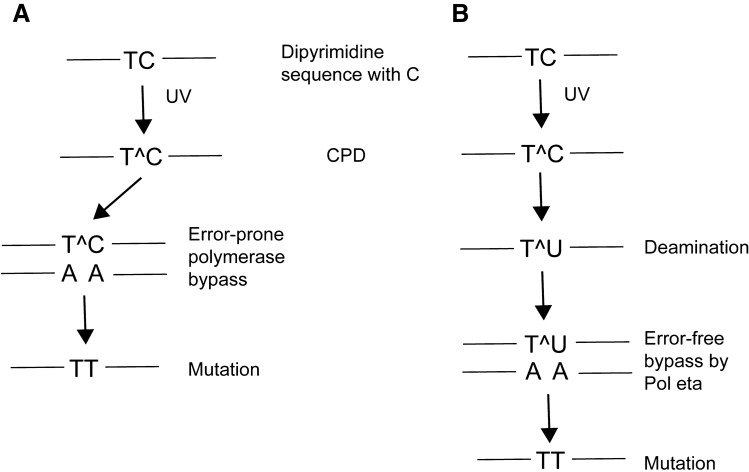
Fig. 2.
Pathways leading to UV mutagenesis at CPDs containing cytosine. a In the error-prone DNA synthesis pathway, a DNA polymerase bypasses the CPD by insertion of an incorrect adenine base across the cytosine leading to C to T mutations. b In the deamination-bypass pathway, the CPD that has formed at dipyrimidines containing cytosine undergoes hydrolytic deamination to uracil. DNA synthesis past uracil-containing dimers by DNA polymerase eta occurs in an error-free manner by incorporation of adenine across uracil. However, the mutation is fixed due to the deamination event. Note that a similar pathway may operate at CPDs containing 5-methylcytosine. In that case, deamination leads to the formation of thymine within the dimers followed by error-free Pol eta bypass of the lesion. UV-induced CC to TT mutations may arise from double cytosine or 5-methylcytosine deamination events