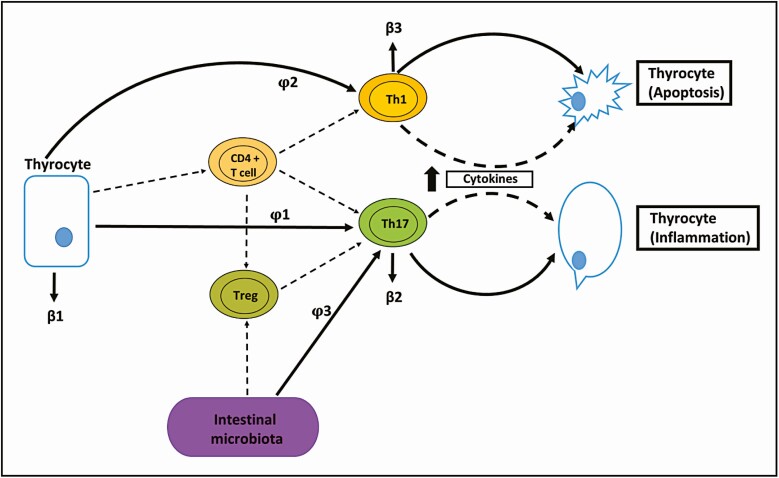
Figure 1.
Schematic representation of simulation model for the Hashimoto autoimmune thyroiditis disease process. In the thyroid gland, thyrocytes mediate the differentiation of CD4+ T-helper (TH) cells into subpopulations of specific T cells (TH1, TH17, and Treg). The proliferation of TH1 and TH17 lymphocytes activate apoptosis and inflammation of the thyroid tissue, respectively. The gut microbiota regulates the relationship between the effector (TH17) and regulator (Treg) lymphocytes, leading to greater differentiation of pathogenic TH17 lymphocytes and subsequent inflammation. The model also assumes that thyrocytes, TH17 lymphocytes and TH1 lymphocytes have mortality rates β 1, β 2, and β 3. The lymphocytic differentiation process φ 1 and φ 2. The Treg and φ 3 parameters stimulate the differentiation of TH17 lymphocytes.