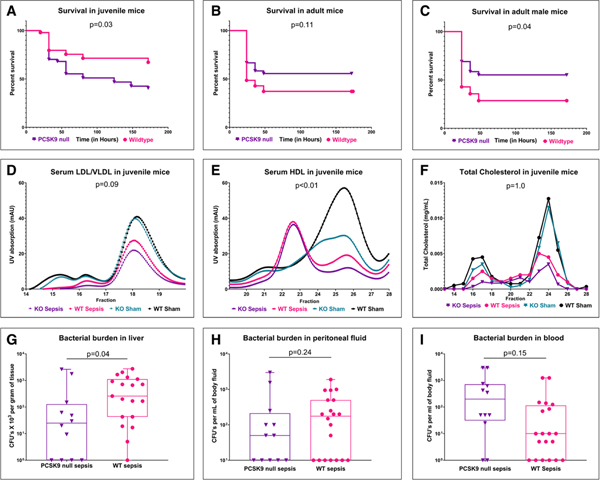
Figure 2.
Impact of proprotein convertase subtilisin/kexin type 9 (PCSK9) loss-of-function in a murine cecal slurry model of sepsis. Seven-day survival in (A) juvenile (14-d old), (B) adult (10–14 wk), (C) adult male (10–14 wk) wildtype (WT) and PCSK9 null mice after induction of sepsis induced by cecal slurry (log-rank test). D, Low-density lipoprotein (LDL)/very-low-density lipoprotein (VLDL), (E) high-density lipoprotein (HDL) concentrations, (F) total cholesterol in juvenile PCSK9 null and WT mice with and without sepsis (analysis of variance [ANOVA]). Bacterial burden (G) in liver (H) peritoneal fluid, and (I) blood, depicted as bacterial colony-forming units (CFUs) in log10 scale (ANOVA). p values shown are for differences between PCSK9 null and WT control mice with sepsis on multiple comparison testing. KO = knockout, UV = ultraviolet.