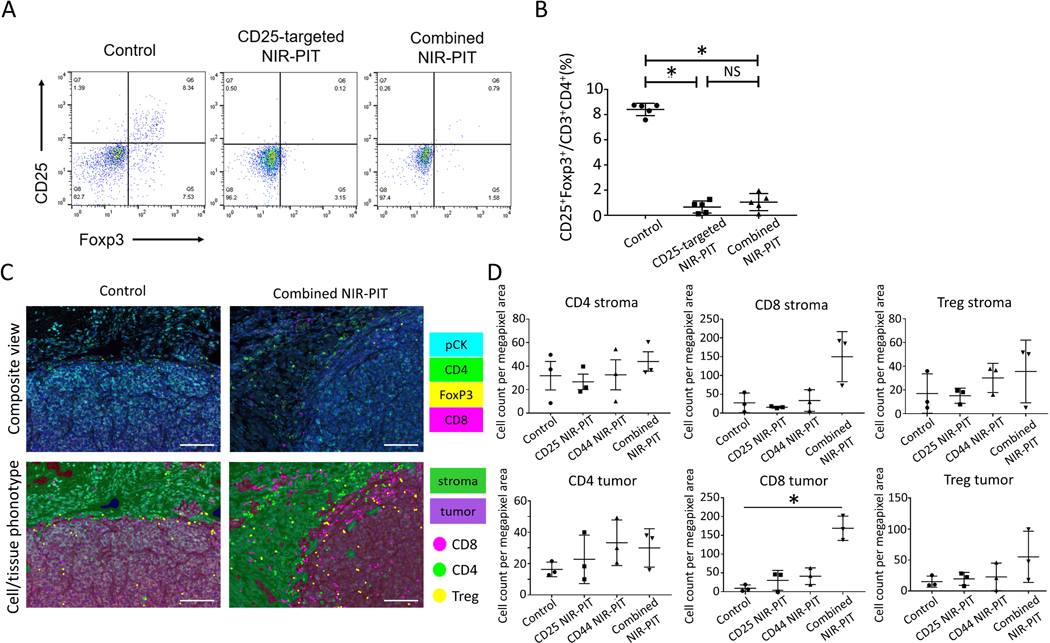
Figure 3. Immune correlative and functional effects of NIR-PIT in MC38-luc tumor-bearing mice.
A. Representative dot plots of live, FOXP3+CD25+CD4+ T cells via flow cytometry in MC38-luc tumors (1 day after NIR light irradiation) treated with CD25-targeted NIR-PIT, combined CD44- and CD25-targeted NIR-PIT, and control tumors. B. Cell count ratios of CD25+FOXP3+ cells in CD3+ CD4+ cells within the tumors (n=5/group from single experiment, mean+/− SEM, *p<0.05, Tukey-Kramer test; NS: not significant. C. Representative multi-color immunofluorescence images (×200) for CD8+ T cells, CD4+ T cells, and Tregs infiltrating in TME of MC38-luc tumors (7 days after NIR light irradiation, n=3/group) treated with CD25-targeted NIR-PIT, CD44-targeted NIR-PIT, combined CD44- and CD25- targeted NIR-PIT (right side), and control tumors (left side). CD8+ cells, CD4+FOXP3– cells, and CD4+FOXP3+ cells were regarded as CD8+ T cells, CD4+ T cells, and Tregs, respectively. Scale bar represents 100um. D. Cell counts per megapixel in multi-color immunofluorescence images to quantitatively evaluate CD4+ T cells, CD8+ T cells, and Tregs infiltrating into the TME. (n=3/group from single experiment, mean+/− SEM, *p<0.05, t-test.