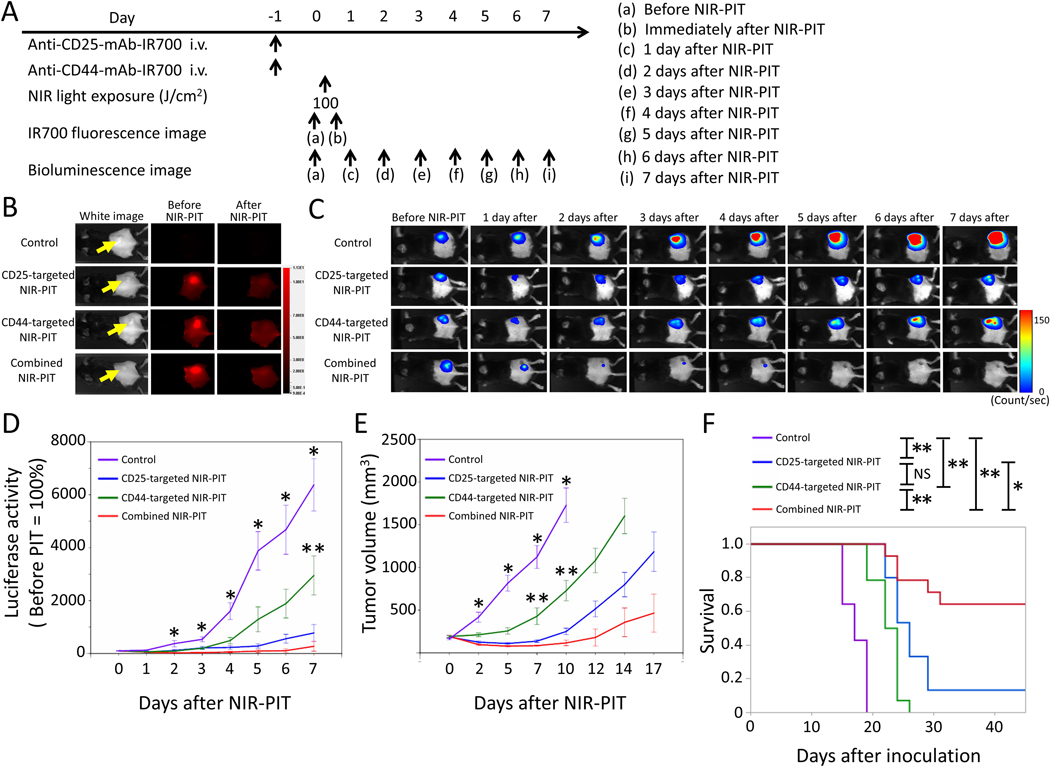
Figure 4. In vivo effect of CD25- and/or CD44-targeted NIR-PIT in MC38-luc tumors.
A. NIR-PIT regimen. Bioluminescence and fluorescence images were obtained at each time point as indicated. B. Real-time in vivo IR700 fluorescence imaging of tumor-bearing mice before and approximately 10 minutes after NIR-PIT. The yellow arrows indicate the tumor locations. C. In vivo bioluminescence imaging of tumor-bearing mice before and after NIR-PIT at the indicated timepoints. D. Quantitative analysis of luciferase activity before and after NIR-PIT in tumor-bearing mice. n≥10/group, mean+/− SEM, *p<0.05, control vs. the other groups, Tukey-Kramer test; **p<0.05, CD44-taregeted NIR-PIT vs. combined NIR-PIT group, Tukey-Kramer test. E. Tumor growth in control and all NIR-PIT–treated groups. n≥10/group, mean+/− SEM, *p<0.05, control vs. the other groups, Tukey-Kramer test; **p<0.05, CD44-targeted NIR-PIT vs. combined NIR-PIT group, Tukey-Kramer test. F. Survival curves for control and NIR-PIT–treated groups. n≥10/group, *p<0.05, **p<0.01, Log-rank test; NS: not significant.