Figure 3: Lysine acylations are chemically diverse and recognized by unique domains.
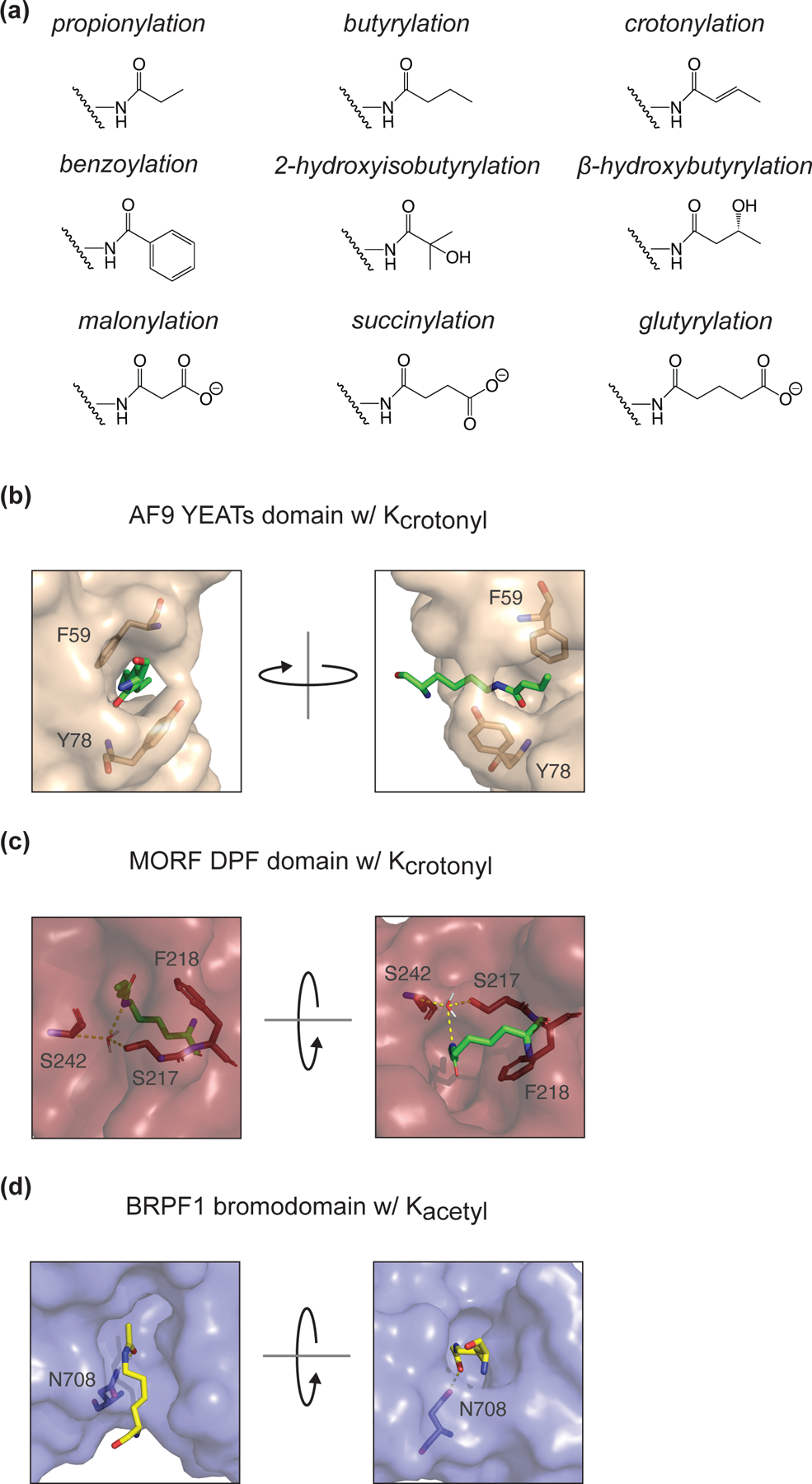
(A) Chemical structures for all identified histone lysine acylations. (B) Crystal structure diagram of Kcrotonyl in the YEATs domain binding pocket of H. sapiens AF9 (PDB: 5HJB). π-stacking is facilitated by residues F59 and Y78. (C) Crystal structure diagram of Kcrotonyl in the DPF domain binding pocket of H. sapiens MORF (PDB: 6OIE). S217 and S242 make polar contacts (mediated by a water molecule) with the crotonylated lysine. F218 improves specificity for Kcro over Kacetyl through π-stacking. (D) Crystal structure diagram of Kacetyl in the bromodomain binding pocket of H. sapiens BRPF1 (PDB: 5FFV). N708, a conserved residue in bromodomains, makes the sole polar contact with the acetylated lysine.
