Figure 1. Associations of proteins with incidence of myocardial infarction, ischemic stroke, and heart failure.
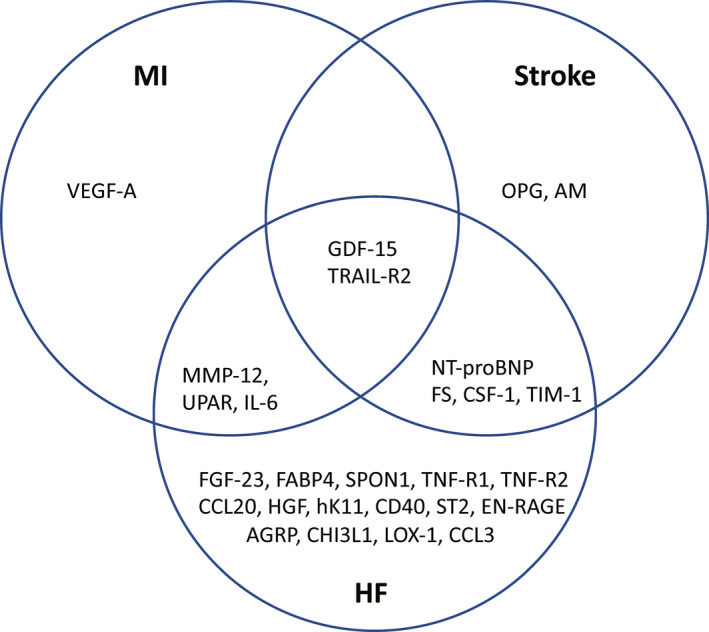
Venn diagram. Only false discovery rate‐adjusted statistically significant associations are shown. AGRP indicates Agouti‐related protein; AM, adrenomedullin; CCL3, C‐C motif chemokine 3; CCL20, C‐C motif chemokine 20; CD40, CD40L receptor; CHI3L1, chitinase‐3‐like protein 1; CSF‐1, macrophage colony‐stimulating factor 1; EN‐RAGE, protein S100‐A12; FABP4, fatty acid binding protein‐4; FGF‐23, fibroblast growth factor 23; FS, follistatin; GDF‐15, growth/differentiation factor 15; HF, heart failure; HGF, hepatocyte growth factor; hK11, kallikrein‐11; IL‐6, interleukin‐6; LOX‐1, lectin‐like oxidized LDL receptor 1; MI, myocardial infarction; MMP‐12, matrix metalloproteinase‐12; NT‐proBNP, N‐terminal pro‐B‐type natriuretic peptide; OPG, osteoprotegerin; SPON1, spondin‐1; ST2, ST2 protein; TIM‐1, T‐cell immunoglobulin and mucin domain 1; TNF‐R1, TNF receptor‐1; TRAIL‐R2, TNF‐related apoptosis‐inducing ligand receptor 2; UPAR, urokinase plasminogen activator surface receptor; and VEGF‐A, vascular endothelial growth factor A.
