Figure 2. Inflammation was attenuated in CCR2‐KO or double‐KO, while CypD‐KO showed residual inflammation.
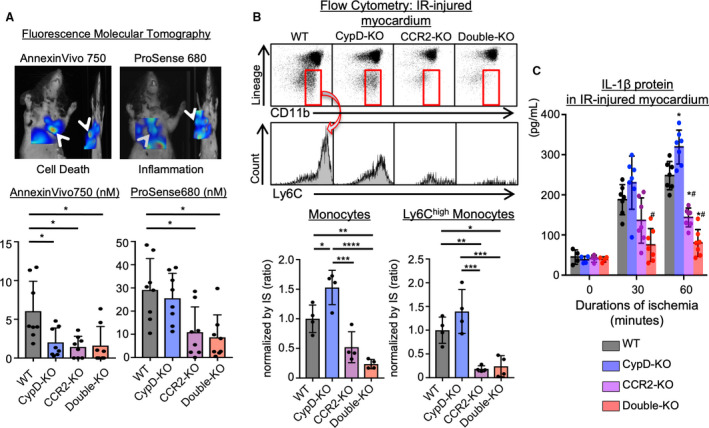
A, Dual channel fluorescence molecular tomography demonstrating cell death (AnnexinVivo750) and protease activity (ProSense680) after ischemia‐reperfusion injury. Bar graphs show quantitative data represented as mean±SD (n=8 per group). *P<0.01, 1‐way ANOVA. B, Ischemia‐reperfusion‒injured myocardium was subjected to flow cytometric analysis. The numbers of monocytes were normalized by IS. Ly6Chigh activated monocytes were decreased in CCR2‐KO or double‐KO mice, whereas CypD‐KO showed larger numbers of total monocytes. The data are mean±SD (n=4 per group). *P<0.05, **P<0.01, ***P<0.001, ****P<0.0001, 1‐way ANOVA. *P<0.05 vs wild‐type, #P<0.05 vs CypD‐knockout, 1‐way ANOVA. C, IL‐1β protein levels in the ischemia‐reperfusion‒injured myocardium measured by ELISA. The data are mean±SD (n=4–7 per group). CCR2‐KO indicates C‐C chemokine receptor 2‐knockout mice; CypD‐KO, cyclophilin D‐knockout mice; Double‐KO, cyclophilin‐D/C‐C chemokine receptor 2‐double knockout mice; IL‐1β, interleukin‐1β; IR, ischemia‐reperfusion; IS, infarct size; and WT indicates wild‐type mice.
