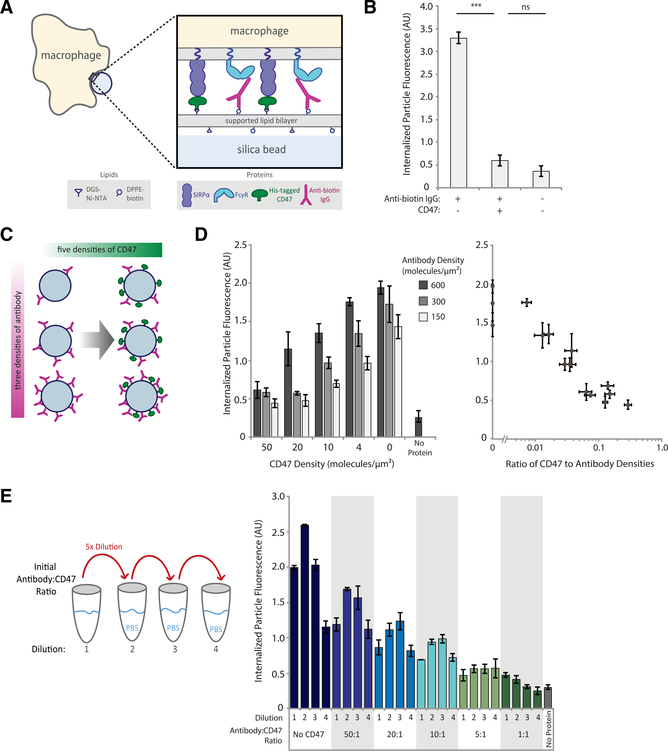
Figure 1. Phagocytosis is dependent on ratio of activating antibody to inhibitory CD47.
(A) Experimental setup of the phagocytosis assay of cell-like target particles by RAW 264.7 macrophages.
(B) Quantification of average internalized, SLB-coated target particle fluorescence shows phagocytosis of protein-coated targets as compared with empty (lipid-only) targets. Each condition is the average of three independent experiments representing a total of >300 cells. Bars represent means ± SEM. Conditions were compared with two-tailed Student’s t test. ***p < 0.001.
(C) Experimental setup of target particles with different anti-biotin IgG and CD47 densities. SLB-coated particles were incubated with 15 different combinations of anti-biotin IgG and CD47 concentrations, in addition to a no-protein (lipid-only) control.
(D) Internalized target particle fluorescence quantification for conditions outlined in (C) (left panel). Data replotted as a function of CD47:antibody ratio (right panel). Each condition is the average of three independent experiments representing a total of >300 cells. Bars represent means ± SEM.
(E) Different anti-biotin IgG to CD47 ratios were created at high concentration, then serially diluted 5-fold, three times, creating a total of four concentrations for each ratio. Internalized target-particle fluorescence was quantified for phagocytosis of each particle ratio. Each condition is the average of three independent experiments representing a total of >300 cells. Bars represent means ± SEM.