Fig. 1 |. IDR-containing GBPLs are essential for plant defence.
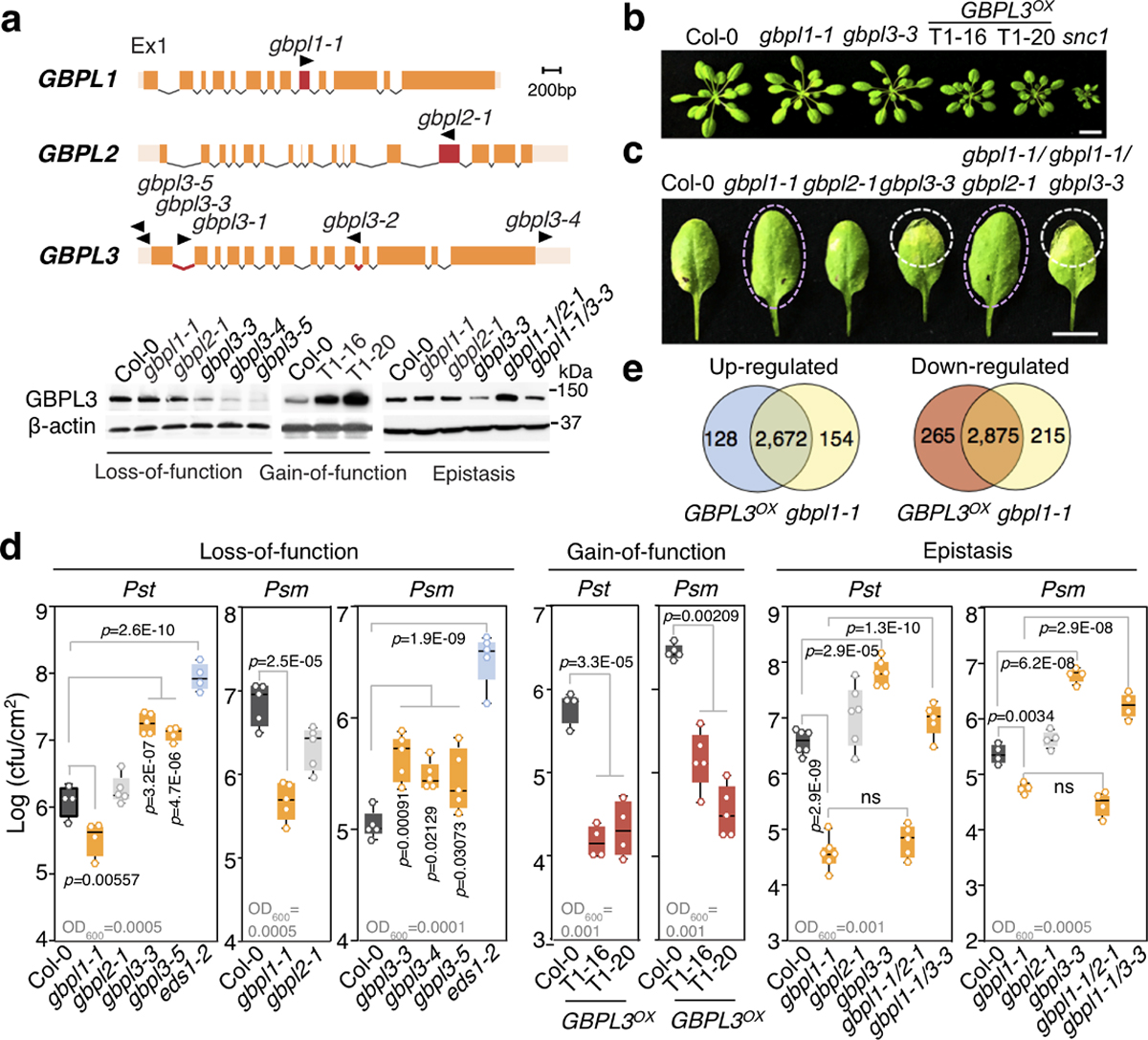
a, Top, structures of Arabidopsis GBPL genes. Positions of T-DNA insertions are in red with triangles indicating transposon direction. Bottom, immunoblot of endogenous GBPL3 levels in T-DNA mutants, overexpression lines (Col-0/pGBPL3::GBPL3 T1–16 and T1–20) and epistatic crosses. Ponceau staining of the large RuBisCO subunit (55 kDa) served as loading control for overexpression lines; β-actin immunoblot served as loading control for the other samples. Ex1, exon 1. b, Growth of five-week-old plants. snc1 mutant, autoimmunity control. Scale bar, 1 cm. c, Representative resistant and susceptible disease phenotypes (dashed circles) of plants infected with Psm ES4326. Scale bar, 1 cm. d, Titre of Psm ES4326 and Pst DC3000 on day 3 of infection. Inoculum density is shown above the x axis (OD600 is optical density at 600 nm). Comparison of mean by one-way ANOVA (Bonferroni post hoc correction). NS, not significant. Centre lines show mean, box edges delineate 25th and 75th percentiles and bars extend to minimum and maximum values. Individual data points represent biologically independent samples. e, Venn diagram of differentially expressed genes in GBPL3OX (T1–20) and gbpl1–1 versus wild type.
