Extended Data Fig. 11 |. GBPL3 enlists a monopartite NLS motif to target the nucleus where it engages Mediator subunits and excludes CDK8 for LLPS-driven immunity.
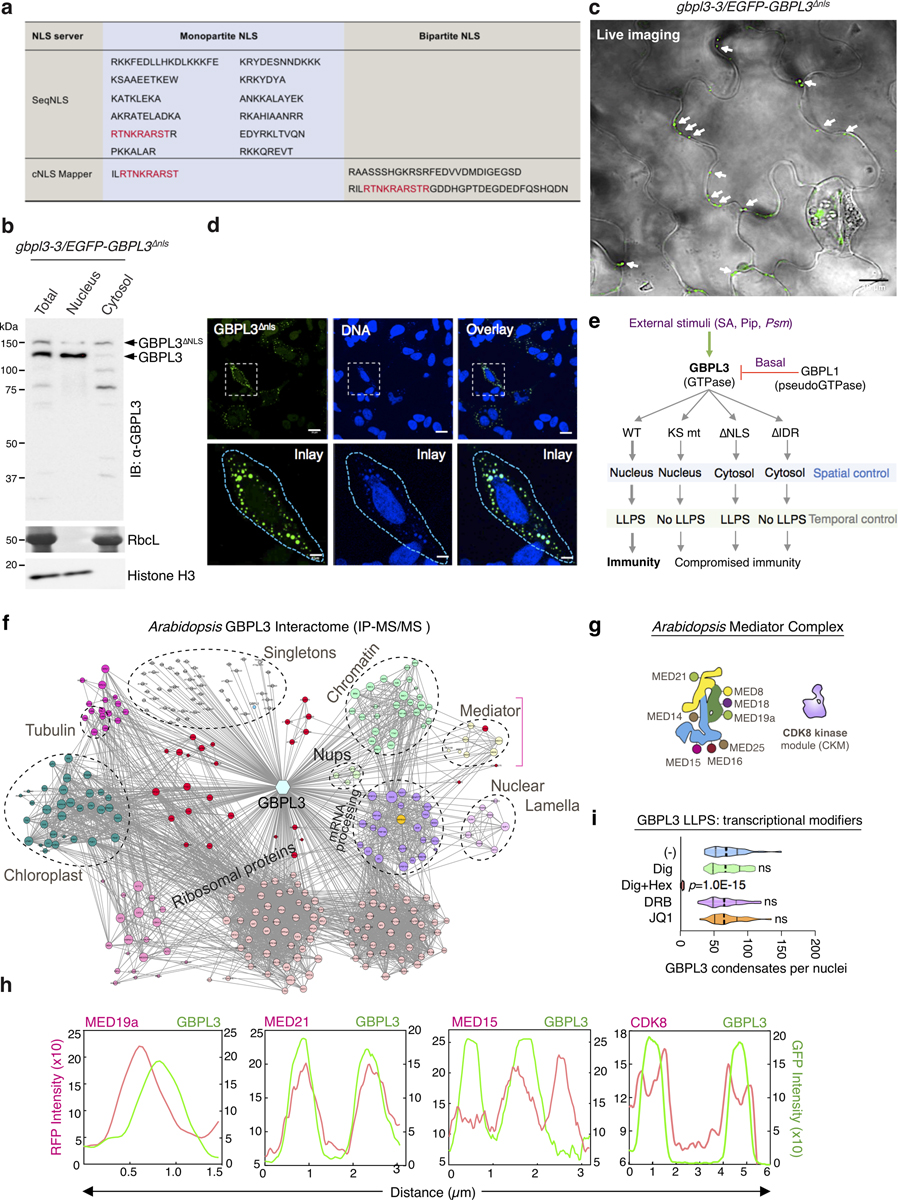
a, NLS motifs in GBPL3. Monopartite and bipartite NLS motifs were predicted via two web servers (SeqNLS and cNLS mapper). Shared sequences in red. b, Subcellular fractionation of gbpl3–3/35S::EGFP-GBPL3ΔNLS plants. RbcL (Ponceau staining) and Histone H3 are cytosol and nuclear controls, respectively. c, Live cell imaging of gbpl3–3/35S::EGFP-GBPL3ΔNLS plant leaves under basal conditions. Image overlay of GFP and DIC channels. Arrows, cytosolic condensates formed by EGFP–GBPL3ΔNLS. Bar, 10 μm. d, Immunofluorescence of CMV::EGFP-GBPL3ΔNLS in HeLa cells. Bar, 20 μm (top) and 5 μm (bottom). e, Spatiotemporal model derived from GBPL3 functional mutagenesis analysis. f, Combinatory GBPL3 interactome in Arabidopsis from co-IP candidates using Col-GBPL3-Flag plants under basal conditions and publicly available data sets (http://plants.proteincomplexes.org/). Node size denotes degree of protein–protein interactions. Classes of GBPL3 interactors grouped by colour-coding. Bracket denotes Mediator complex interactions. g, Different subunits associated with each region of the Arabidopsis Mediator complex (head [yellow], middle [green] and tail [blue] modules) and CDK8 kinase module. h, Line profile (colocalization) of fluorescence intensity for CDK8, MED15, MED19a and MED21 co-expressed with GBPL3 in (Fig. 4b). These head, middle and tail Mediator subunits directly overlap and interact with GBPL3 in leaf cell PPI profiling. CDK8 is excluded and surrounds GBPL3, as seen in line profiling. i, Effects of digitonin (10 μg/ml), digitonin plus 1,6-hexanediol (Hex, 5%), DRB (100 μM) and JQ1 (1 μM) on GBPL3 LLPS in live HeLa cells 2 h after treatment (n = 30 biologically independent cells/treatment). One-way ANOVA test with Bonferroni post hoc correction.
