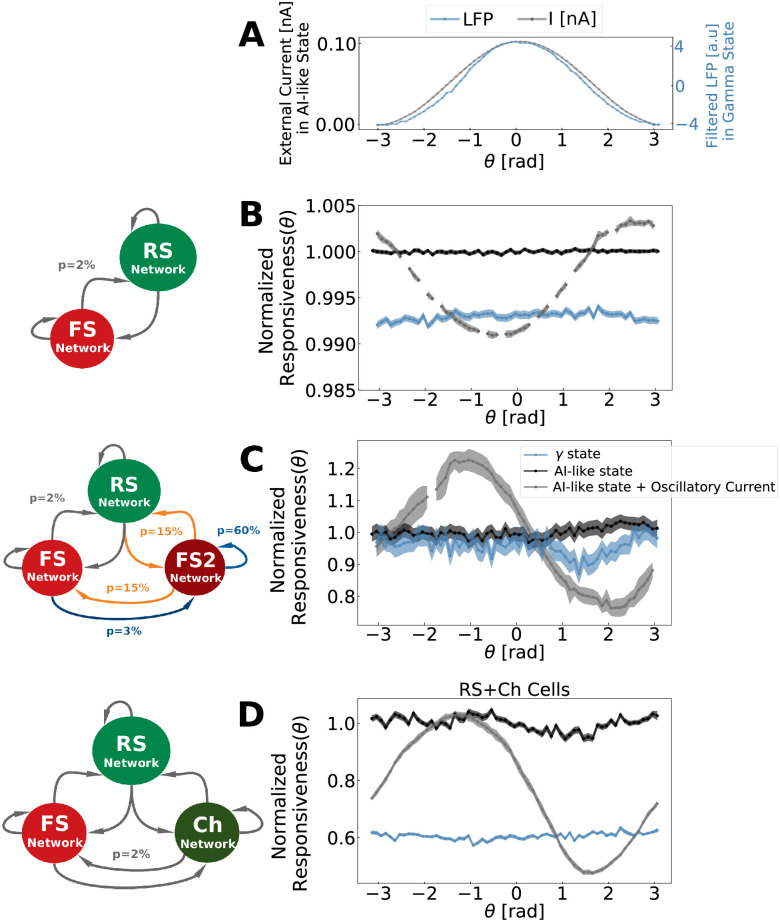
Fig 8. Phase-dependent network response.
A: External oscillatory current applied at AI-like state as function of its oscillation phases (gray curve) and the filtered LFP measured during Gamma states as function of its oscillation phases (blue curve). All networks received a current oscillating from 0 to 0.1 nA in a sinusoidal manner with a Gamma frequency Fγ. To match the Gamma oscillation frequency generated by each network, the frequency of the external current applied to PING and CHING networks was Fγ = 40 Hz, while the one applied to ING network was Fγ = 55 Hz. The LFP depicted is the one from PING network. ING and CHING also displayed a similar LFP pattern. B: PING Network phase-dependent response C: ING Network phase-dependent response. D:CHING Network phase-dependent response. The phase-dependent network response was calculated according to Eq 6, in a time window of duration T equal to one Gamma cycle (T = 25ms for the PING and CHING Networks and T = 18ms for ING). Responses measured inside AI-like activity (outside Gamma bursts) are shown in black, and in gray when the networks received a supplementary oscillatory external current. Responses measured inside Gamma bursts are displayed in blue. All curves were normalized by the average response inside AI-like activity without external current modulation. Solid lines indicate the average, and the shaded region indicates the standard error of the mean. The curves were calculated based on the output of 12000 simulations (120 positions of the Gaussian stimulus in 100 numerical seeds for external Poissonian drive). The Gaussian stimulus used had an amplitude of 50 Hz and standard deviation of 1 ms.