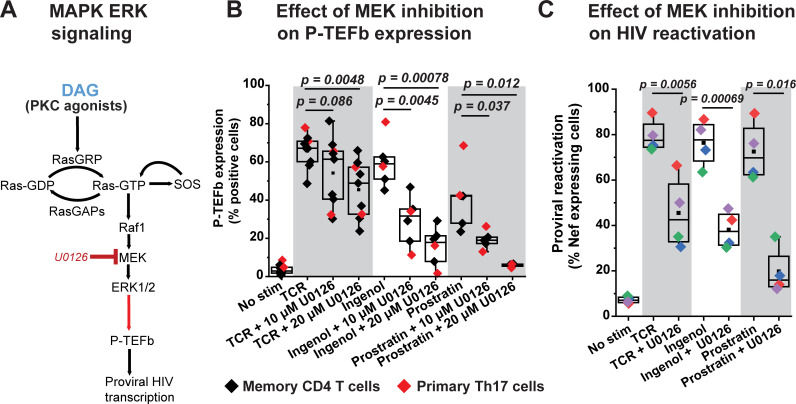
Fig 6. Inducible P-TEFb expression and proviral reactivation in primary T cells are mediated by the MAPK ERK pathway.
(A) Proposed scheme for the intracellular stimulation of P-TEFb expression in primary T cells by PKC agonists or TCR-generated diacylglycerol (DAG) leading up to the reactivation of HIV from latency. (B) The MEK inhibitor U0126 substantially blocks expression of active P-TEFb in primary CD4+ T cells in response to treatment with PKC agonists but modestly inhibits P-TEFb expression in response to TCR co-stimulation. Memory CD4+ or primary Th17 cells were treated or not for 30 min with U0126 at the indicated concentrations prior to TCR co-stimulation with anti-CD3/anti-CD28 Dynabeads or challenge with either 50 nM ingenol or 1 μM prostratin for 24 h. Cells were then analyzed by flow cytometry for P-TEFb expression following immunostaining using fluorophore-conjugated antibodies towards CycT1 and pSer175 CDK9. (C) U0126 substantially retards proviral reactivation in primary Th17 cells in response to TCR co-stimulation or challenge with PKC agonists. Latently infected Th17 cells prepared using naïve CD4+ T cells from two different donors were pretreated or not with 20 μM U0126 for 30 min prior to TCR co-stimulation with anti-CD3/anti-CD28 Dynabeads or challenge with 50 nM ingenol or 1 μM prostratin for 24 h. Cells were analyzed by flow cytometry following immunostaining using a fluorophore-conjugated antibody towards HIV Nef. All the p values shown in B and C were calculated using a two-tailed Student’s t test.