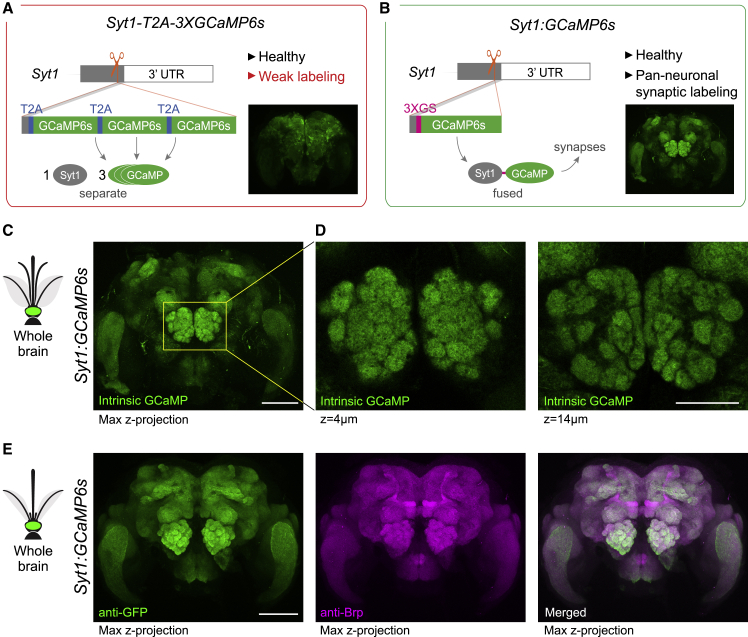
Figure 2.
Generation of a pan-neuronal, synaptically localized GCaMP line for neural imaging in Ae. aegypti
(A and B) Summary schematics for two alternative strategies showing construct design and outcome (red border indicates failure for reason given in red lettering; green border indicates success). The first strategy (A) involved in-frame insertion of three copies of GCaMP6s separated by T2A ribosomal skipping sequences designed to generate separate Syt1 and GCaMP proteins (Syt1-T2A-3XGCaMP6s). Expression appeared pan-neuronal (inset), but GCaMP expression was too weak for neural imaging. The second strategy (B) involved in-frame insertion of GCaMP6s preceded by a 3XGS linker designed to generate a Syt1-GCaMP fusion protein (Syt1:GCaMP6s). By concentrating GCaMP at presynaptic sites, this approach produced a healthy line bright enough for imaging. Insets show anti-GFP staining (A) or intrinsic GCaMP fluorescence (B) in adult brains. Both constructs also included a screening marker (3XP3-dsRed, not shown).
(C and D) Intrinsic GCaMP fluorescence in brain (C) and antennal lobe (D, two z planes) of Syt1:GCaMP6s heterozygous male.
(E) Anti-Brp (neuropil) and anti-GFP staining in brain of Syt1:GCaMP6s heterozygous female. Scale bars, 100 μm (C and E) and 50 μm (D).