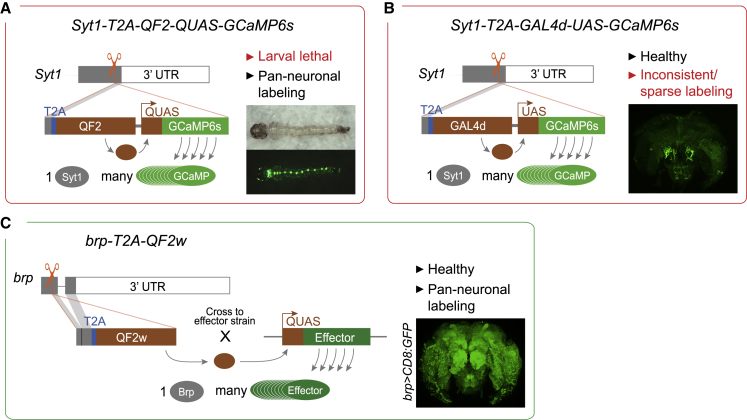
Figure 4.
Generation of a pan-neuronal driver line in Ae. aegypti
Each panel provides a summary schematic for one of the three alternative strategies (red border, failed; green border; successful).
(A and B) The first two strategies involved in-frame insertion of transcriptional activators near the end of the native Syt1 locus designed to generate separate Syt1 and QF2 (A) or GAL4d (B) proteins. Corresponding GCaMP6s effector elements were included in tandem to enable rapid one-step testing of pan-neuronal expression. Insets show intrinsic GCaMP fluorescence in larva (A) or anti-GFP staining in adult brains (B). Both approaches failed for reasons provided (red font).
(C) The third strategy involved in-frame insertion of the QF2w transcriptional activator near the end of the native brp locus, designed to result in more modest levels of expression of the weaker transcriptional activator. Inset shows anti-GFP staining in brain of adult female from cross between brp-T2A-QF2w and QUAS-CD8:GFP. All donor constructs also included a screening marker (3XP3-dsRed, not shown).