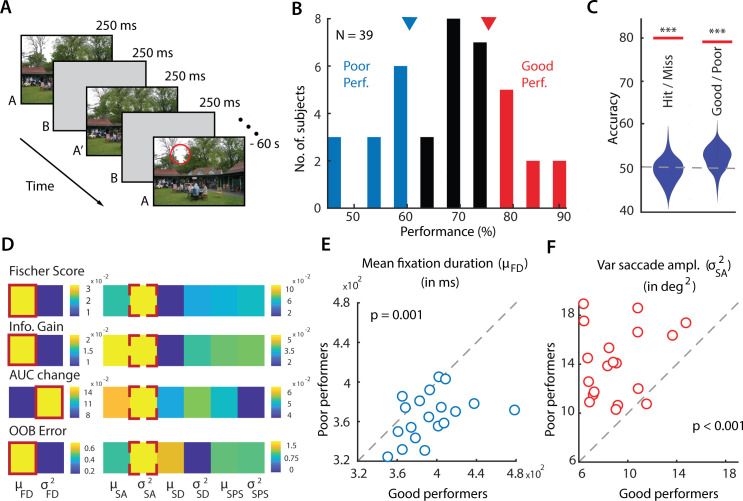
Fig 1. Gaze metrics predict success in a change blindness experiment.
A. Schematic of a change blindness experiment trial, comprising a sequence of alternating images (A, A’), displayed for 250 ms each, with intervening blank frames (B) also displayed for 250 ms (“flicker” paradigm), repeated for 60 s. Red circle: Location of change (not actually shown in the experiment). All 20 change image pairs tested are available in Data Availability link. B. Distribution of success rates of n = 39 participants in the change blindness experiment. Red and blue bars: good performers (top 30th percentile; n = 9) and poor performers (bottom 30th percentile; n = 12), respectively. Inverted triangles: Cut-off values of success rates for classifying good (red) versus poor (blue) performers. C. Classification accuracy, quantified with area-under-the-curve (AUC), for classifying trials as hits versus misses (left horizontal line) and performers as good versus poor (right horizontal line), obtained with a support vector machine classifier. Violin plots: Null distributions of classification accuracies based on a permutation test (*** p<0.001). Error bars: Clopper-Pearson binomial confidence intervals. D. Feature selection measures for identifying the most informative features that distinguish good from poor performers. From top to bottom: Fisher score, Information gain, Change in area-under-the-curve (AUC) and bag of decision trees (for details, see Feature Selection Metrics in the Materials and Methods). Brighter colors indicate more informative features. Solid red outline: most informative feature in the fixation feature subgroup (left); dashed red outline: most informative feature in the saccade feature subgroup (right). FD—fixation duration, SA—saccade amplitude, SD—saccade duration, SPS—saccade peak speed. μ and σ2 denote mean and variance of the respective parameter. E. Distribution of mean fixation duration (μFD, in milliseconds) across 19 change images for good performers (x-axis) versus poor performers (y-axis); one change image pair, successfully detected by all performers, was not included in these analyses (see text). Each data point denotes average value of μFD, across each category of performers, for each image tested. Dashed diagonal line: line of equality. p-value corresponds to significant difference in mean fixation duration between good and poor performers. F. Same as in E, but comparing variance of saccade amplitudes (in squared degrees of visual angle) for good versus poor performers. Other conventions are the same as in panel E.