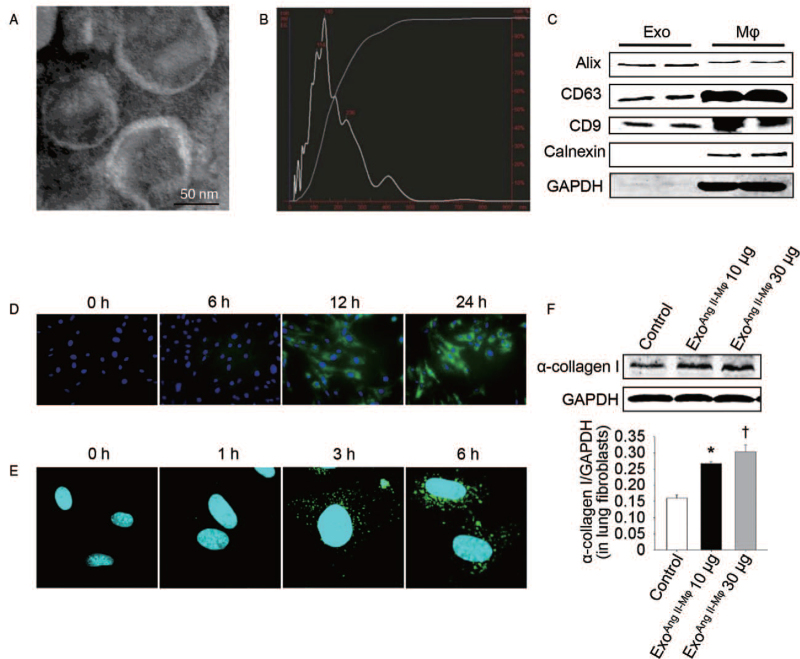
Figure 3.
Exosomes mediate the effect of macrophage-induced α-collagen I synthesis in lung fibroblasts. (A) Morphology of macrophage exosomes determined by transmission electron microscopy (scale bar: 50 nm). (B) Nanoparticle tracking analysis (NTA) for quantitative measurement of isolated exosome particles. (C) Exosomal markers analyzed by western blot. (D) Fibroblasts were co-cultured with PKH67-labeled macrophages or (E) incubated with PKH67-labeled exosomes extracted from macrophages at different time points. Then the fibroblasts were stained with DAPI and analyzed by fluorescent microscopy or confocal microscopy, respectively. (F) Fibroblasts were treated with exosomes from Ang II-stimulated macrophages in doses of 10 μg/mL (exoAng II-Mϕ 10 μg) and 30 μg/mL (exoAng II-Mϕ 30 μg) for 24 h. Western blot was used to detect α-collagen I protein level. n = 3 independent experiments, ∗P < 0.05 vs. control group; †P < 0.05 vs. exoAng II-Mϕ10 μg group. Ang II: Angiotensin II; DAPI: 4-6 Diamidino-2-phenylindole; Exo: Exosomes; GAPDH: Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase; Mϕ: Macrophages.