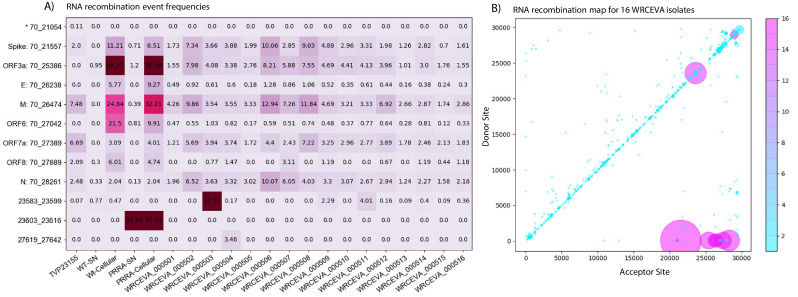
Figure 5. Tiled-ClickSeq identifies sub-genomic mRNAs, structural variants, and defective-RNAs.
(A) A table of the most common RNA recombination events found using Tiled-ClickSeq to study ‘World Reference Center for Emerging Viruses and Arboviruses’ (WRCEVA) isolates. The recombination junctions are indicated on the left of the table, with their relative frequencies indicated in the table and colour-matched for each sample analyzed. All canonical sgmRNAs are found with their open-reading frame (ORF) indicated, in addition to one non-canonical sgmRNA (*). Three common structural variants including two deletions in spike protein and a deletion in ORF7a were also detected. (B) Unique RNA recombination events are plotted for 16 WRCEVA isolates as a scatter plots whereby the upstream ‘donor’ site is plotted on the y-axis and a downstream ‘acceptor’ site is plotted on x-axis. The read count for each unique RNA recombination event is indicated by the size of the point, while the number of samples in which this each RNA recombination event is found is indicated by the colour-bar. Insertions/duplication/back-splicing events are found above the x = y axis, while deletions and RNA recombination events yielding sgmRNAs are found below.