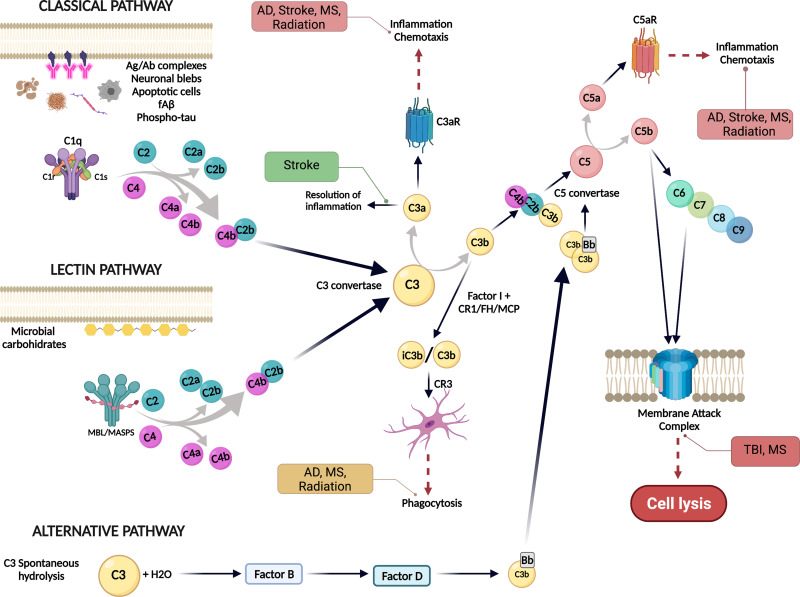
Figure 1.
Overview of the complement system activation pathways. The complement system can be activated by three different pathways: classical, lectin or the alternative pathway. The presence of neuronal blebs, fAß, phosphor-tau, apoptotic cells or antigen-antibody complexes can bind to C1 complex and activate the classical pathway. The lectin pathway is activated when microbial carbohydrates bind mannan-binding lectin (MBL) in complex with MASP1/2 and the alternative pathway is activated by a spontaneous hydrolysis of C3. All three pathways converge at C3, that is cleaved by the C3 convertase into C3a and C3b. C3a promotes chemotaxis via C3aR, while C3b could bind to C4b2b to form the C5 convertase and cleave C5 into C5a and C5b. C5a is a potent inflammatory effector that promotes chemotaxis and activation through C5aR1, while C5b binds to C6, C7, C8 and C9 to form the membrane attack complex (MAC) to induce cell lysis. Green boxes indicate a beneficial role of the complement system, orange boxes mean that the effect can be either beneficial or detrimental if dysregulated and red boxes denote a detrimental effect of the complement system associated with specific conditions. Created with BioRender.com.