Figure 3:
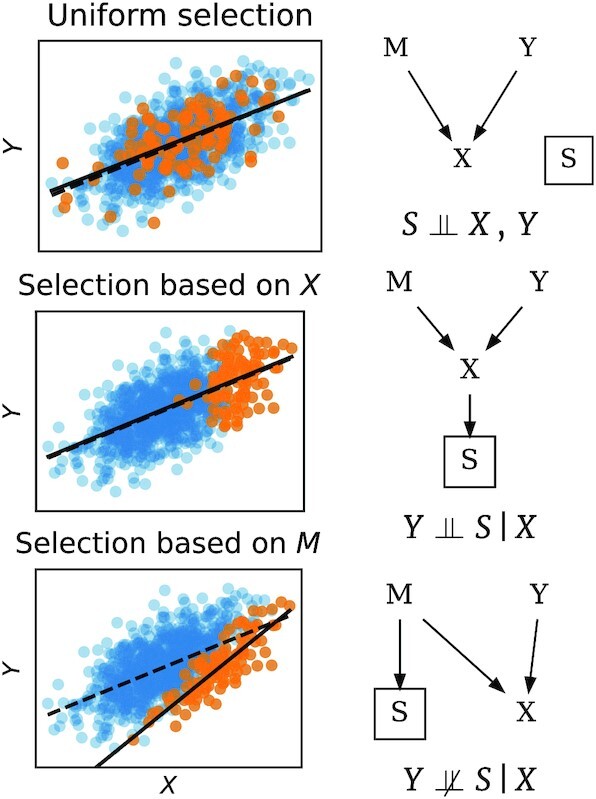
Sample selection bias: three examples. On the right are graphs giving conditional independence relations [40]. Y is the lesion volume to be predicted (i.e., the output). M are the imaging parameters, e.g., contrast agent dosage. X is the image, and depends both on Y and M (in this toy example X is computed as 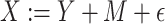 , where ϵ is additive noise). S indicates that data are selected to enter the source dataset (orange points) or not (blue points). The symbol
, where ϵ is additive noise). S indicates that data are selected to enter the source dataset (orange points) or not (blue points). The symbol 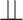 means independence between variables. Preferentially selecting samples results in a dataset shift (middle and bottom row). Depending on whether
means independence between variables. Preferentially selecting samples results in a dataset shift (middle and bottom row). Depending on whether 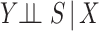 , the conditional distribution of
, the conditional distribution of 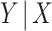 —here lesion volume given the image—estimated on the selected data may be biased or not.
—here lesion volume given the image—estimated on the selected data may be biased or not.
