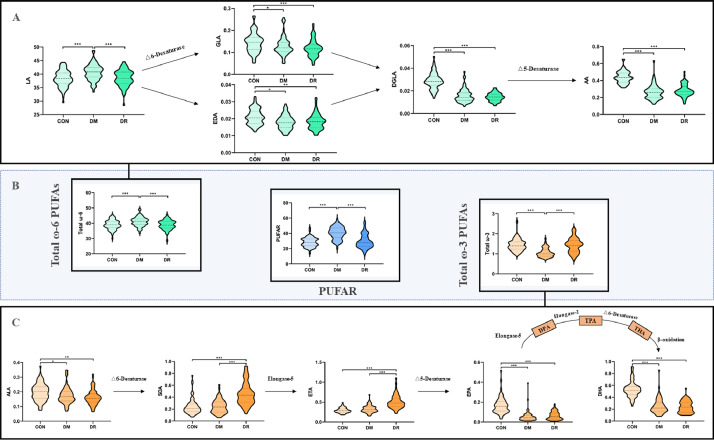
Fig. 1.
Biosynthesis pathways and relative concentration of PUFAs as well as PUFAR amongst the three groups.
CON: healthy control; DM: type 2 diabetic patients without diabetic retinopathy; DR: type 2 diabetic patients with diabetic retinopathy; PUFAs: serum polyunsaturated fatty acids; LA: linoleic acid; GLA: γ-Linolenic acid; EDA: eicosadienoic acid; DGLA: dihomo-γ-linolenic acid; AA: arachidonic acid; ALA: α-Linolenic acid; SDA: stearidonic acid; ETA: eicosatetraenoic acid; EPA: eicosapentaenoic acid; DPA: docosapentaenoic acid; TPA: 12–0-tetradecanoylphorbol-13-acetate; THA: tetracosahexaenoic acid; DHA: docosahexaenoic acid; Total ω-6 PUFAs: the sum of LA, GLA, EDA, DGLA, and AA; Total ω-3 PUFAs: the sum of ALA, SDA, ETA, EPA, and DHA; PUFAR: serum ω-6/ω-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids ratio. The colour in green, orange, and blue refer to the family of ω-6, ω-3 PUFAs, and PUFAR, respectively. The shade of colour represents the disease status. * p < 0·05; ** p < 0·01; *** p < 0·001 (For interpretation of the references to colour in this figure legend, the reader is referred to the web version of this article.).