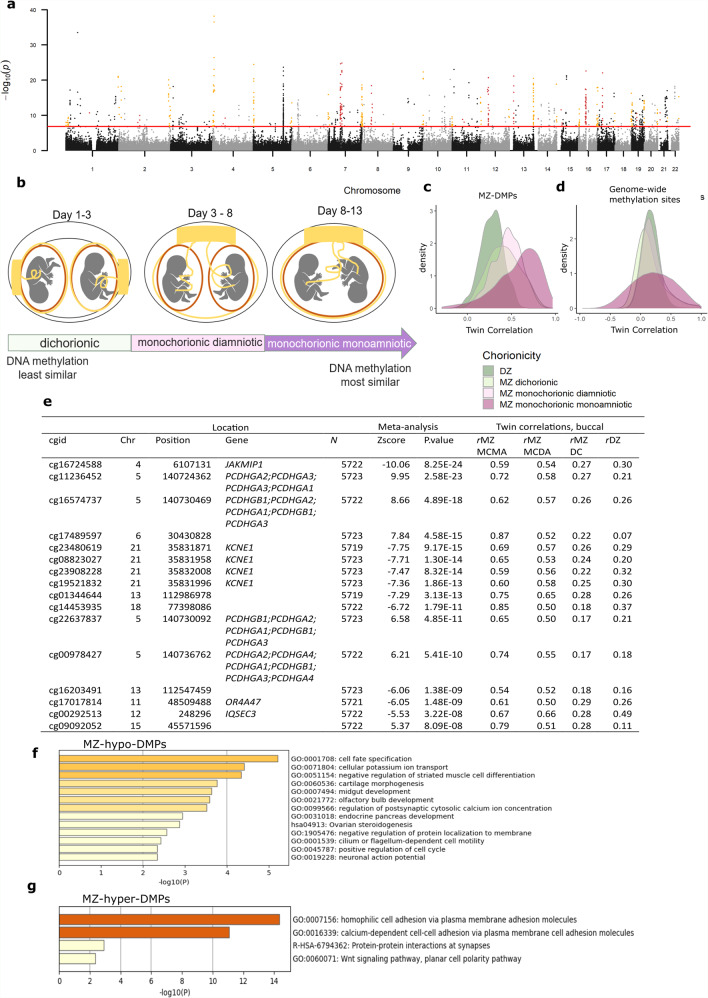
Fig. 2. MZ twinning DMPs identified in a meta-analysis of data from 5723 twins.
a Manhattan plot of the EWAS meta-analysis based on whole blood DNA methylation data from five twin cohorts (total sample size = 5723) that identified 834 MZ-DMPs. The red horizontal line denotes the epigenome-wide significance threshold (Bonferroni correction). Dark red dots highlight significant DMPs near centromeres. Orange dots highlight significant DMPs near telomeres. b Dichorionic (DC) MZ twins have separate chorions, amnions, and placentas. Monochorionic diamniotic (MCDA) MZ twins have separate amnions and a common chorion and placenta. Monochorionic monoamniotic (MCMA) have a common chorion, amnion, and placenta. It has been hypothesized that DC MZ twins result from separation soon after fertilization, whereas MC twins are thought to result from separation ≥3 days after fertilization, with MCMA twins arising later than MCDA twins. c Density plots of twin correlations for the differentially methylated positions in monozygotic twins (MZ-DMPs) identified in the EWAS meta-analysis illustrate that the overall distribution of twin correlations at MZ-DMPs show the following pattern: rMZ-MCMA > rMZ-MCDA > rMZ-DC. d Twin correlations for genome-wide autosomal methylation sites do not follow this pattern. MZ monozygotic twins, DZ dizygotic twins. e MZ-DMPs with larger correlations in monochorionic MZ twins compared to dichorionic MZ twins. The CpGs were selected by three criteria (1) rMZ-MCMA > rMZ-MCDA > rMZ-DC; (2) rMZ-MCDA > 0.5; (3) rMZ-DC < 0.2. cgid = Illumina CpG identifier. Chr = chromosome; rMZ-MCMA = correlation in monozygotic monochorionic monoamniotic pairs. rMZ-MCDA = correlation in monozygotic monochorionic diamniotic pairs. rMZ-DC = correlation in monozygotic dichorionic pairs. f–g Pathway enrichment analysis results based on the nearest genes of the 834 Bonferroni-significant MZ-DMPs identified in the meta-analysis. f Top enriched gene ontology (GO) pathways for MZ-hypo-DMPs (differentially methylated positions with a lower methylation level in monozygotic twins). The darker the color, the stronger the enrichment. g Top enriched gene ontology (GO) pathways for MZ-hyper-DMPs (differentially methylated positions with a higher methylation level in monozygotic twins). The darker the color, the stronger the enrichment.