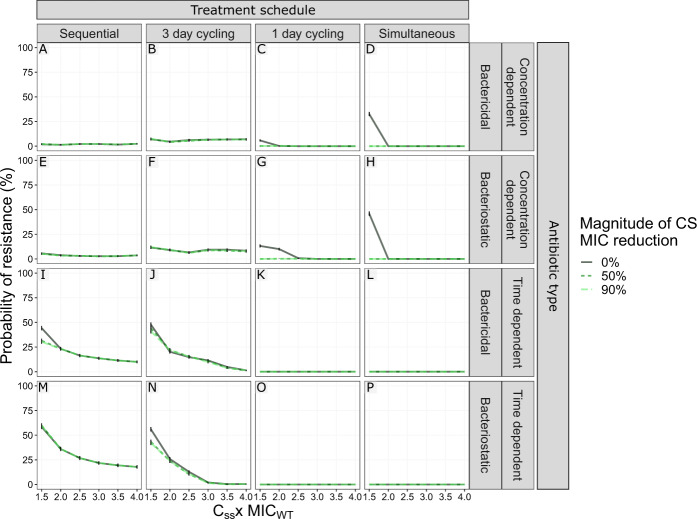
Fig. 6. The effect of antibiotic steady-state concentrations (Css) in relation to different levels of collateral sensitivity (CS) on the probability of resistance at the end of treatment (PoR).
The simulation revealed that CS had the largest impact on PoR for Css close to MIC of the wild-type strain (MICWT). Css was expressed as a factor difference from the MICWT. For the dosing regimen using simultaneous administrated antibiotics the Css represent the total antibiotic Css, where the individual antibiotics were dosed at 0.5 x Css. PoR of RAny, defined as the presence of any resistant subpopulation, was estimated at the end of treatment for treatments using different designs (columns) and antibiotic types (rows). Each simulated scenario was realized n = 500 times. Colour and line-type indicate the magnitude of reciprocal CS simulated. Data are presented as mean PoR with the error bars that represent the standard error of the estimation.