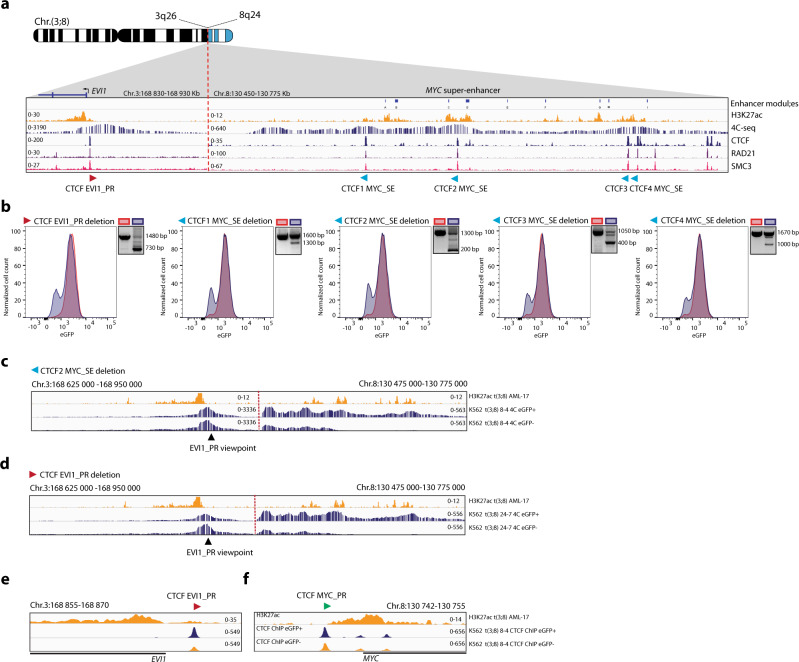
Fig. 5. CTCF binding sites in MYC SE are involved in the interaction with the EVI1 promoter.
a Schematic overview of the t(3;8) model, zoom-in on the breakpoint with 3q26 on the left and 8q24 on the right (separated by a dotted red line). The EVI1 promoter and the MYC super-enhancer are illustrated by H3K27ac ChIP-seq data of primary t(3;8) AML (AML-17) in orange on top. Below in blue, 4C-seq data showing the interaction pattern between the EVI1 promoter and the MYC enhancer modules in K562 t(3;8) clone 24-7. The lower 3 tracks show ChIP-seq data of CTCF (blue in K562 t(3;8) clone 24-7) and the cohesin subunits RAD21 (purple) and SMC3 (pink), both in K562 WT and retrieved from ENCODE62. b Flow cytometry plot of K562 EVI1-eGFP t(3;8) clone 8-4 cells after deletion of the indicated CTCF binding site (blue graph), and in red the control cells (no Cas9). On the right of the graph, the deletion is shown by PCR. Source data are provided as a Source Data file. c Chromatin interaction at the MYC SE in eGFP+ (upper blue track) and eGFP− cells (lower blue track), shown by 4C-seq with the EVI1 promoter as viewpoint, after deletion of the MYC SE CTCF2 binding site. The top H3K27ac ChIP-seq track (orange) shows the presence of the active EVI1 promoter and the modules of the MYC SE. d Chromatin interaction at the MYC SE in eGFP+ (upper blue track) and eGFP− cells (lower blue track), shown by 4C-seq with the EVI1 promoter as viewpoint after deletion of the EVI1 PR CTCF binding site (indicated by the red arrow, corresponding to the CTCF EVI1_PR locus in A). The top H3K27ac ChIP-seq track (orange) shows the presence of the active EVI1 promoter and the modules of the MYC SE. e CTCF ChIP-seq presenting CTCF occupancy in eGFP− cells (clone 8-4, orange) compared to eGFP + cells (clone 8-4, blue) at the CTCF binding site upstream of the EVI1 promoter after deletion of this CTCF EVI1_PR site. The top H3K27ac ChIP-seq track (orange) shows the presence of the active EVI1 promoter and the modules of the MYC SE. f The same CTCF ChIP-seq tracks are shown (clone 8-4), but now presenting unchanged CTCF occupancy at the CTCF binding site upstream of the MYC promoter.