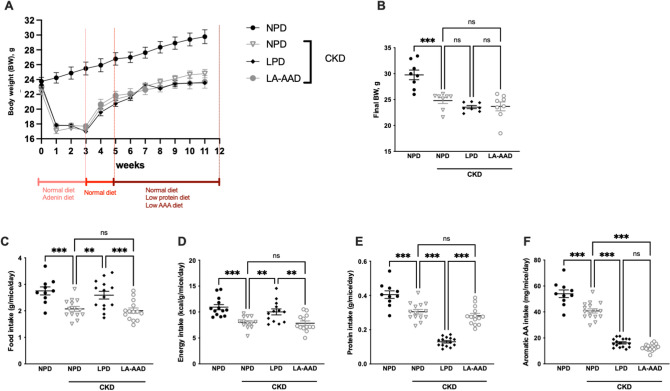
Figure 1.
Food, energy, protein and aromatic amino acids intakes according to each specific diet and renal condition. Body weight evolution (A), final body weight (B), food intake (C), energy intake (D), protein intake (E) and aromatic amino-acid intake (F) in control mice fed with normoproteic diet (NPD) and chronic kidney disease (CKD) mice fed with NPD, low protein diet (LPD) or low aromatic amino-acid diet (LA-AAD). Data are presented as mean ± SEM for n = 10–13 animals in each group. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001 versus CKD-NPD; (ANOVA and Dunnett post hoc test).